“PTO In The United States”
Faith Goff
In recent years, a largely debated economic topic in the U.S. has been if businesses should be required to provide paid leave of absences for employees during a family member’s illness or the birth of their child. Those who support paid leaves argue that situations may arise, out of workers’ control, making it difficult or even impossible for them to be present during these times. Meanwhile, the opposing side states that it’s unfair to the companies who are compensating someone without the exchange of labor, especially those which may not have the money or enough employees to make up for the loss. Some even think that this benefit can easily be abused with dishonest claims.
There are also people who fall somewhere in the middle, most of which believe that child birth, a “personal choice,” should not be considered for paid leave and that it creates an unfair disadvantage for employees who decide against raising a family. As they automatically receive less time off, this understandably creates a controversial imbalance in the workplace. However, many commenters fail to recognize that, not only is pregnancy often not a personal choice, it’s also a major life-altering event that can only be held off for so long. Working couples that wish to have children shouldn’t be expected to let this desire subside just because they have to worry about the financial constraint that would come with a lack of income despite being employed.
Another important note in this debate is that the United States currently stands as the only industrialized country which doesn’t require sick leave from its companies. This makes it legal for American businesses to have individual choices in the matter (appropriate for the country’s system of economy), allowing a lack of inequality in the privileges of employees. Considering the government remains uninvolved with this particular issue, it also provokes the question of whether or not officials should step in and create a new law regarding paid time off across the nation.
In my opinion, paid leave of absence should be required for all companies, whether it’s due to sickness, maternity, or any other uncontrollable situation. While it’s true that employees are capable of manipulating such a privilege, they should all be trusted until proven deceitful, as with anything else. As for the other workers who aren’t receiving the same amount of time off, it must be taken into consideration the fact that these individuals aren’t being paid during additional vacation days, they’re being paid during a time of grief, pain, or overall importance to their life. Thus, it shouldn’t be argued that the others are being treated unjustly, especially when they could easily fall under similar circumstances in the future. It’s certainly not a matter of “special treatment” or one group of employees receiving higher benefits than the other, but rather showing respect towards dedicated workers who have earned full-time employment at the corporation and stumbled into unfortunate circumstances which have prohibited them from operating efficiently in the workplace.
Works Cited
“Paid Sick Leave Poll Results.” ISideWith, www.isidewith.com/poll/1476448702.
“Paid Maternity Leave: Inside the Debate.” Business.com, www.business.com/articles/paid-maternity-leave-inside-the-debate-and-what-it-means-for-your-business/.
A collaboration between economics and personal finance classes at Pewaukee High School. All content and views published on here are solely those of the author of the piece and do not represent the views of Pewaukee High School nor the Pewaukee School District.
Thursday, October 25, 2018
Tariffs on Chinese Goods: good or bad?
Tariffs on Chinese Goods: Good or Bad?
Josh Cottrill
In the past couple of months, President Donald Trump has been making remarks about proposing tariffs on Chinese goods in an effort to increase spending on domestic-made goods and services. While that may seem good for the US as it could potentially raise the GDP and promote companies from the United States, The lasting effects on China and their economy, won’t be very good. A very large portion of China’s economy and monetary value comes from all of their exported goods such as toys, food, manufacturing products, and so much more. As a matter of fact they are the number one exporting country in the world at about $2.263 trillion in 2017 as they top the United States which is at about $1.546 trillion. The Chinese trade tariffs will do no good to global economy, as the United States depends greatly on Chinese made products, and as a result of these special taxes, neither country will positively impacted in the long run.

As the supply of the chinese made goods goes down, there will be less demand for people to buy them, so Americans will mostly rely on American made goods, which initially sounds like a good plan for the US economy, however this is projected to only be a temporary change, not a permanent one. COuntries are supposed to interact with other countries, helping them where help is needed, and ultimately making those countries better and better. However, eliminating this interaction between China and America is not a good thing in the long run. CHina makes so many important goods for people all over the world. For example, they make iPhone parts and actually construct the phones themselves as well, they also make a lot of manufacturing equipment such as machines and tools. As a matter of fact, there is an incredible chance that something you have already interacted with today - and even every day- has been made from China. This computer was most likely made in China as well.
Because China has such a large impact on goods everyone uses daily, would you want to pay more money for products? According to www.msn.com, these Chinese goods’ rates are expected to climb to a 25% increase in price by 2019. That means if you want to buy a new iPhone that was made in China, you would have to spend nearly $1400 dollars and that is just insane. Likewise, this would force the American public to not buy from specific companies such as Apple anymore, and due to the fact that millions of people around the US and even around the globe are loyal customers to the brand, means that their sales won’t go down too much, especially when new technology comes out like the new iPhones, Apple watches, and more. As another example, the price of fast food would ultimately increase because all of the machines at fast food restaurants are made in China. Everyone knows how the ice cream machine is always broken at McDonalds, so what if they bout a new ice cream machine at every store, and had to inflate the prices to $2.00 or $2.50 per individual soft serve cone. Ultimately, imposed tariffs on Chinese exported products would not help China, nor the United States respectively. It would only raise prices for everyone because so many products that the public interacts with are made in China, where in total, no one would benefit from this in the long term.
Works Cited
Chinese Official Tells American Investors at a Meeting: We Don't Fear a Trade War with the US, www.msn.com/en-us/money/markets/chinese-official-tells-american-investors-at-a-meeting-we-dont-fear-a-trade-war-with-the-us/ar-BBOJXvC?li=BBnbfcN.
Lee, Xin En. “Trump's Tariffs Threaten to Shatter China's Economy. It Already Has Cracks.” CNBC, CNBC, 24 Sept. 2018, www.cnbc.com/2018/09/24/trumps-trade-war-threatens-chinese-economy-china-already-has-cracks.html.
“Top Exporting Countries Worldwide 2017.” Statista, www.statista.com/statistics/264623/leading-export-countries-worldwide/.
Josh Cottrill
In the past couple of months, President Donald Trump has been making remarks about proposing tariffs on Chinese goods in an effort to increase spending on domestic-made goods and services. While that may seem good for the US as it could potentially raise the GDP and promote companies from the United States, The lasting effects on China and their economy, won’t be very good. A very large portion of China’s economy and monetary value comes from all of their exported goods such as toys, food, manufacturing products, and so much more. As a matter of fact they are the number one exporting country in the world at about $2.263 trillion in 2017 as they top the United States which is at about $1.546 trillion. The Chinese trade tariffs will do no good to global economy, as the United States depends greatly on Chinese made products, and as a result of these special taxes, neither country will positively impacted in the long run.
As the supply of the chinese made goods goes down, there will be less demand for people to buy them, so Americans will mostly rely on American made goods, which initially sounds like a good plan for the US economy, however this is projected to only be a temporary change, not a permanent one. COuntries are supposed to interact with other countries, helping them where help is needed, and ultimately making those countries better and better. However, eliminating this interaction between China and America is not a good thing in the long run. CHina makes so many important goods for people all over the world. For example, they make iPhone parts and actually construct the phones themselves as well, they also make a lot of manufacturing equipment such as machines and tools. As a matter of fact, there is an incredible chance that something you have already interacted with today - and even every day- has been made from China. This computer was most likely made in China as well.
Because China has such a large impact on goods everyone uses daily, would you want to pay more money for products? According to www.msn.com, these Chinese goods’ rates are expected to climb to a 25% increase in price by 2019. That means if you want to buy a new iPhone that was made in China, you would have to spend nearly $1400 dollars and that is just insane. Likewise, this would force the American public to not buy from specific companies such as Apple anymore, and due to the fact that millions of people around the US and even around the globe are loyal customers to the brand, means that their sales won’t go down too much, especially when new technology comes out like the new iPhones, Apple watches, and more. As another example, the price of fast food would ultimately increase because all of the machines at fast food restaurants are made in China. Everyone knows how the ice cream machine is always broken at McDonalds, so what if they bout a new ice cream machine at every store, and had to inflate the prices to $2.00 or $2.50 per individual soft serve cone. Ultimately, imposed tariffs on Chinese exported products would not help China, nor the United States respectively. It would only raise prices for everyone because so many products that the public interacts with are made in China, where in total, no one would benefit from this in the long term.
Works Cited
Chinese Official Tells American Investors at a Meeting: We Don't Fear a Trade War with the US, www.msn.com/en-us/money/markets/chinese-official-tells-american-investors-at-a-meeting-we-dont-fear-a-trade-war-with-the-us/ar-BBOJXvC?li=BBnbfcN.
Lee, Xin En. “Trump's Tariffs Threaten to Shatter China's Economy. It Already Has Cracks.” CNBC, CNBC, 24 Sept. 2018, www.cnbc.com/2018/09/24/trumps-trade-war-threatens-chinese-economy-china-already-has-cracks.html.
“Top Exporting Countries Worldwide 2017.” Statista, www.statista.com/statistics/264623/leading-export-countries-worldwide/.
Airports control your Spending
Airports control your spending
Agastya Asthana
Many people walk through the airports daily in awe of the airport architecture and in the belief that they have full control of the decision they are to make in the future. Airports are designed so that passengers subconsciously spend time and money there. Below are some of the ingenious ways airports generate revenue.
Airport duty-free shops are right outside security. After getting through the security, passengers are rid of the “stresses of waiting in line, removing their belt and shoes, being patted down by a stranger, and perhaps having another rifle through their belongings”(Telegraph). This sense of relief and the retail environment tells your brain it’s time to shop. The airport walkways are curved left most of the time. Many people that enter the airport carry some form of luggage with their right hand and look to their right most of the time; airports exploit this by making walkways curve left and line the right with duty-free stores so that most of the time you are looking at a brightly colored store selling everything you want(Telegraph). Airports estimate that every extra hour spent per person in an airport generates $7 in revenue(Telegraph). Therefore, the Heathrow airport in London makes about $3.6 million in revenue every year(Heathrow).


Those who believe they go to the airport just to catch their flight to a destination will fall victims to the psychological tricks. It is ethical that airports employ these tactics because not everyone has the same cognitive structure and some may not fall susceptible to the tactics, and still the airport has great architecture and makes you feel comfortable which does not come free or cheap. Do you think it is ethical to employ psychological tricks in airports?
Works Cited
“ACI Chief Calls for Greater Airport–Airline Cooperation.” The Moodie Davitt Report, 7 Apr. 2016, www.moodiedavittreport.com/aci-chief-calls-for-greater-airport-airline-cooperation/.
“Dubai Airport Inside Stock Photos and Images.” Alamy, www.alamy.com/stock-photo/dubai-airport-inside.html.
“Heathrow 2015 Financial Results Released with Revenue and Passenger Satisfaction Up.” Your Heathrow - Heathrow Airport Microsite, 8 Aug. 2018, your.heathrow.com/heathrow-revenue-grow-passenger-satisfaction-saws-in-2015/.
Kim, Soo. “The Surprising Reason Why Airport Walkways Bend to the Left.” The Telegraph, Telegraph Media Group, 23 Nov. 2017, www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/lists/how-airports-make-you-spend-duty-free-shopping/.
Agastya Asthana
Many people walk through the airports daily in awe of the airport architecture and in the belief that they have full control of the decision they are to make in the future. Airports are designed so that passengers subconsciously spend time and money there. Below are some of the ingenious ways airports generate revenue.
Airport duty-free shops are right outside security. After getting through the security, passengers are rid of the “stresses of waiting in line, removing their belt and shoes, being patted down by a stranger, and perhaps having another rifle through their belongings”(Telegraph). This sense of relief and the retail environment tells your brain it’s time to shop. The airport walkways are curved left most of the time. Many people that enter the airport carry some form of luggage with their right hand and look to their right most of the time; airports exploit this by making walkways curve left and line the right with duty-free stores so that most of the time you are looking at a brightly colored store selling everything you want(Telegraph). Airports estimate that every extra hour spent per person in an airport generates $7 in revenue(Telegraph). Therefore, the Heathrow airport in London makes about $3.6 million in revenue every year(Heathrow).
Those who believe they go to the airport just to catch their flight to a destination will fall victims to the psychological tricks. It is ethical that airports employ these tactics because not everyone has the same cognitive structure and some may not fall susceptible to the tactics, and still the airport has great architecture and makes you feel comfortable which does not come free or cheap. Do you think it is ethical to employ psychological tricks in airports?
Works Cited
“ACI Chief Calls for Greater Airport–Airline Cooperation.” The Moodie Davitt Report, 7 Apr. 2016, www.moodiedavittreport.com/aci-chief-calls-for-greater-airport-airline-cooperation/.
“Dubai Airport Inside Stock Photos and Images.” Alamy, www.alamy.com/stock-photo/dubai-airport-inside.html.
“Heathrow 2015 Financial Results Released with Revenue and Passenger Satisfaction Up.” Your Heathrow - Heathrow Airport Microsite, 8 Aug. 2018, your.heathrow.com/heathrow-revenue-grow-passenger-satisfaction-saws-in-2015/.
Kim, Soo. “The Surprising Reason Why Airport Walkways Bend to the Left.” The Telegraph, Telegraph Media Group, 23 Nov. 2017, www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/lists/how-airports-make-you-spend-duty-free-shopping/.
Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Navigating Expensive Box Offices
Noah O’Neal
Navigating Expensive Box Offices.
 Our beloved Milwaukee Brewers lost in game seven of the NLCS on Saturday to the LA Dodgers. The series was full of nonstop action and drama between the teams and fans. During the postseason and throughout the NLCS, it became harder and harder for fans to get tickets to the games. The demand for these tickets grew, but the supply did not, there are only so many seats in Miller Park. 41,900 to be exact. As the demand for these play off tickets grew, they also brought with them quite a large price tag. But all of this is now in the past, let’s focus on the next big thing, the World Series.
Our beloved Milwaukee Brewers lost in game seven of the NLCS on Saturday to the LA Dodgers. The series was full of nonstop action and drama between the teams and fans. During the postseason and throughout the NLCS, it became harder and harder for fans to get tickets to the games. The demand for these tickets grew, but the supply did not, there are only so many seats in Miller Park. 41,900 to be exact. As the demand for these play off tickets grew, they also brought with them quite a large price tag. But all of this is now in the past, let’s focus on the next big thing, the World Series.
According to StubHub.com, the cheapest tickets you can get for game one of the World Series cost $424.00 for each ticket. At Fenway Park this puts you in the back row of the right field grandstand in section five. Arguably the seats with the worst view of home plate. StubHub also says that the most expensive tickets are $25,000.00 each. This would put you in row A1, right behind home plate. Now let’s look a little deeper into the economics behind all of this. Why would someone pay over $400 to barely see the game. Or why pay $25,000 just to watch a three hour baseball game. Also, how do owners determine the prices of each ticket?
 World Series tickets are an inelastic good. The increase in prices causes less then a 1% change in the quantity demanded meaning it’s inelastic. People will still pay observed amounts of money to see these games because quantity is limited. This tells owners that they and raise the prices of tickets and people will still come and buy them. But now the question is, how high is too high for ticket prices? This is where they factor in marginal utility. Marginal utility is a way to determine how much satisfaction a customer will receive from a product. This is why that the worst seats in the house are still so expensive. Even though that person can barely see the games, they are still satisfied with spending $424 just to be at a World Series baseball games. This also applies to the person behind home plate. They are satisfied with paying $25,000 for those seats because the marginal utility received is worth $25,000 to that sold out fan. Also now a broke sold out fan.
World Series tickets are an inelastic good. The increase in prices causes less then a 1% change in the quantity demanded meaning it’s inelastic. People will still pay observed amounts of money to see these games because quantity is limited. This tells owners that they and raise the prices of tickets and people will still come and buy them. But now the question is, how high is too high for ticket prices? This is where they factor in marginal utility. Marginal utility is a way to determine how much satisfaction a customer will receive from a product. This is why that the worst seats in the house are still so expensive. Even though that person can barely see the games, they are still satisfied with spending $424 just to be at a World Series baseball games. This also applies to the person behind home plate. They are satisfied with paying $25,000 for those seats because the marginal utility received is worth $25,000 to that sold out fan. Also now a broke sold out fan.
So, throughout the rest of the World Series, and other big events, look closer at the big price tag on tickets. The prices rise because they are an inelastic good, and the supply is limited. They also go up because the marginal utility is greater than a typical games, and lastly that some people just have way too much disposable income.
“StubHub!” StubHub, www.stubhub.com/boston-red-sox-tickets-boston-red-sox-boston-fenway-park-10-23-2018/event/103753469/?sort=quality+desc&tktbkt=1.
Navigating Expensive Box Offices.
According to StubHub.com, the cheapest tickets you can get for game one of the World Series cost $424.00 for each ticket. At Fenway Park this puts you in the back row of the right field grandstand in section five. Arguably the seats with the worst view of home plate. StubHub also says that the most expensive tickets are $25,000.00 each. This would put you in row A1, right behind home plate. Now let’s look a little deeper into the economics behind all of this. Why would someone pay over $400 to barely see the game. Or why pay $25,000 just to watch a three hour baseball game. Also, how do owners determine the prices of each ticket?
So, throughout the rest of the World Series, and other big events, look closer at the big price tag on tickets. The prices rise because they are an inelastic good, and the supply is limited. They also go up because the marginal utility is greater than a typical games, and lastly that some people just have way too much disposable income.
Works Cited
Durst, Nicholas. “DGS Staff Predictions: Who Will Win The 2018 World Series? • Double G Sports.” Double G Sports, 2 Oct. 2018, doublegsports.com/who-will-win-the-2018-world-series/.“StubHub!” StubHub, www.stubhub.com/boston-red-sox-tickets-boston-red-sox-boston-fenway-park-10-23-2018/event/103753469/?sort=quality+desc&tktbkt=1.
LeBron James Leaving Cleveland
LeBron James Leaving Cleveland
BJ Wallace
LeBron James left Cleveland just over 3 months ago and his absence doesn’t just hurt the team’s success but the city as a whole economically. If his move causes the same economic downfall as his first move in 2010, the city would lose an estimated $300 million as a whole.
Why would one player leaving an NBA team cause such a loss in a cities economy? While I know this would require a response more well-versed in macroeconomics, there are several microeconomic components through the reasoning.

First, the merchandise sold by the Cleveland Cavaliers was 25% accounted for by LeBron James jerseys and other products. Imagine you are selling any one product such as a type of crop, and there is a storm that rids of 25% of your field. This is a very significant decrease in supply. This leftward shift of the supply curve would cause the new quantity demanded to decrease.
The biggest reason for a decrease in economic value when LeBron leaves is that going to a Cleveland Cavaliers game is a complementary product to many of the local businesses such as many well known restaurants. When the demand for the cavaliers tickets go down, which will inevitably happen when the best basketball player in the world leaves, the demand for the compliments will also go down. Just being in the city and experiencing the downtown area is also a compliment and when all of these businesses are getting less customers, the economy will be in decline. Even the owner of the Cavaliers, Dan Gilbert, will experience this decline because he has invested in a well-known casino named Jack Casino. This casino has had a total revenue of of $1.26 billion in the last 6 years. Below is the number of restaurants within one mile of the stadium in the years that LeBron was in Cleveland and in Miami. As you can see, there are more restaurants when he is present. With these restaurants brings jobs which greatly benefit the economy.

Finally, a more in depth proof of the drop in price of the game tickets (the main source of profit for the team) can be shown through the marginal utility of the consumer. We know that most consumers will buy a product up until the point where marginal utility is equal to the marginal revenue or the price. Without the electrifying presence of LeBron James, the marginal utility for each game you go to will decrease. This will create one of three outcomes. Either the prices of tickets will stay the same so less people would attend the games, the prices of tickets will decrease significantly and the same number of people will attend the games, or somewhere in the middle. In each scenario, the total revenue of the organization is lower than what it was in 2017 because either the price decreases while quantity sold stays the same, price stays the same and the quantity sold decreases, or both.
It is amazing that one person can have such a large effect on the economy of a city by just being there playing a game. Not only does it affect the team’s revenue through merchandise and ticket sales, but also it affects the surrounding businesses. We will have to wait a few more months to see the final effect of his move.
Rooney, Kate, and Leslie Josephs. “How LeBron's Move West Could Tip Parts of Cleveland's Economy South.” CNBC, CNBC, 10 July 2018, www.cnbc.com/2018/07/02/lebron-james-move-will-hurt-clevelands-winning-record--but-its-econ.html.
Rovell, Darren. “LeBron James Is Worth Hundreds of Millions to the Cavs and Cleveland.” ESPN, ESPN Internet Ventures, 13 June 2018, www.espn.com/nba/story/_/id/23769496/lebron-james-worth-millions-economy-cleveland.
Scott, Dylan. “LeBron James Means a Lot to Cleveland - and Its Economy.” Vox, Vox, 1 June 2017, www.vox.com/2017/6/1/15724252/lebron-james-economic-impact-cleveland-miami.
BJ Wallace
LeBron James left Cleveland just over 3 months ago and his absence doesn’t just hurt the team’s success but the city as a whole economically. If his move causes the same economic downfall as his first move in 2010, the city would lose an estimated $300 million as a whole.
Why would one player leaving an NBA team cause such a loss in a cities economy? While I know this would require a response more well-versed in macroeconomics, there are several microeconomic components through the reasoning.
First, the merchandise sold by the Cleveland Cavaliers was 25% accounted for by LeBron James jerseys and other products. Imagine you are selling any one product such as a type of crop, and there is a storm that rids of 25% of your field. This is a very significant decrease in supply. This leftward shift of the supply curve would cause the new quantity demanded to decrease.
The biggest reason for a decrease in economic value when LeBron leaves is that going to a Cleveland Cavaliers game is a complementary product to many of the local businesses such as many well known restaurants. When the demand for the cavaliers tickets go down, which will inevitably happen when the best basketball player in the world leaves, the demand for the compliments will also go down. Just being in the city and experiencing the downtown area is also a compliment and when all of these businesses are getting less customers, the economy will be in decline. Even the owner of the Cavaliers, Dan Gilbert, will experience this decline because he has invested in a well-known casino named Jack Casino. This casino has had a total revenue of of $1.26 billion in the last 6 years. Below is the number of restaurants within one mile of the stadium in the years that LeBron was in Cleveland and in Miami. As you can see, there are more restaurants when he is present. With these restaurants brings jobs which greatly benefit the economy.
Finally, a more in depth proof of the drop in price of the game tickets (the main source of profit for the team) can be shown through the marginal utility of the consumer. We know that most consumers will buy a product up until the point where marginal utility is equal to the marginal revenue or the price. Without the electrifying presence of LeBron James, the marginal utility for each game you go to will decrease. This will create one of three outcomes. Either the prices of tickets will stay the same so less people would attend the games, the prices of tickets will decrease significantly and the same number of people will attend the games, or somewhere in the middle. In each scenario, the total revenue of the organization is lower than what it was in 2017 because either the price decreases while quantity sold stays the same, price stays the same and the quantity sold decreases, or both.
It is amazing that one person can have such a large effect on the economy of a city by just being there playing a game. Not only does it affect the team’s revenue through merchandise and ticket sales, but also it affects the surrounding businesses. We will have to wait a few more months to see the final effect of his move.
Works Cited
Banks, Alec. “The LeBron James Effect: An Economy Built on One Man.” Highsnobiety, Highsnobiety, 14 July 2018, www.highsnobiety.com/p/lebron-james-effect-econony/.Rooney, Kate, and Leslie Josephs. “How LeBron's Move West Could Tip Parts of Cleveland's Economy South.” CNBC, CNBC, 10 July 2018, www.cnbc.com/2018/07/02/lebron-james-move-will-hurt-clevelands-winning-record--but-its-econ.html.
Rovell, Darren. “LeBron James Is Worth Hundreds of Millions to the Cavs and Cleveland.” ESPN, ESPN Internet Ventures, 13 June 2018, www.espn.com/nba/story/_/id/23769496/lebron-james-worth-millions-economy-cleveland.
Scott, Dylan. “LeBron James Means a Lot to Cleveland - and Its Economy.” Vox, Vox, 1 June 2017, www.vox.com/2017/6/1/15724252/lebron-james-economic-impact-cleveland-miami.
The Rise of American-Made Clothing
The Rise of American-Made Clothing
Written by: Nik D.
 On June 1st, 2017, the United States imposed 10% tariffs on aluminum and 25% on steel being exported to Europe, and as a retaliatory response, the European Union placed 25% tariffs on European-made clothing being exported to the United States. Recently, the Trump Administration set out to try and “force” companies to produce goods within the United States in hope of a more self-sustaining economy. In order to do this, they placed large tariffs on an aluminum and steel being imported to the United States. In a retaliatory response, the European Union slapped 25% tariffs on jeans, shorts, t-shirts, and synthetic woven trousers being exported to the United States ( a tariff is an extra tax added to a good being exported or imported). Some of these clothing goods are shown on the right. A common output from tariffs is that they change the number of goods being imported or exported). According to Rick Helfenbein, the chief executive/president of the American Apparel and Footwear Association, “‘Made in USA’ apparel... will suffer as a direct result of this action by the Trump administration”. I believe that Helfenbein is on point with the outcome effects of these tariffs, and believe that they are not beneficial for our economy and greatly hurt individual clothing companies.
On June 1st, 2017, the United States imposed 10% tariffs on aluminum and 25% on steel being exported to Europe, and as a retaliatory response, the European Union placed 25% tariffs on European-made clothing being exported to the United States. Recently, the Trump Administration set out to try and “force” companies to produce goods within the United States in hope of a more self-sustaining economy. In order to do this, they placed large tariffs on an aluminum and steel being imported to the United States. In a retaliatory response, the European Union slapped 25% tariffs on jeans, shorts, t-shirts, and synthetic woven trousers being exported to the United States ( a tariff is an extra tax added to a good being exported or imported). Some of these clothing goods are shown on the right. A common output from tariffs is that they change the number of goods being imported or exported). According to Rick Helfenbein, the chief executive/president of the American Apparel and Footwear Association, “‘Made in USA’ apparel... will suffer as a direct result of this action by the Trump administration”. I believe that Helfenbein is on point with the outcome effects of these tariffs, and believe that they are not beneficial for our economy and greatly hurt individual clothing companies.
When looking on a smaller scale, these clothing tariffs can be devastating to clothing companies; in specific they affect implicit/explicit costs, profit, as well as the marginal cost/revenue of the companies. The production of the clothing being produced within the United States rather than overseas leads to greater explicit costs. A majority of the increased explicit costs are due to higher wages needed to pay to the workers in the United States. Yes, it is good that the businesses are producing product within our country, but then again they are doing so less efficiently than they would if the product was produced overseas. The increase in wages outweighs the costs of producing within the United States (such as less transportation cost due to no international transportation), so these tariffs are not beneficial whatsoever. The production of the clothing, as well as the material costs, are close to the exact same as they are overseas, so it is the increase in worker wages that is responsible for the greater explicit costs. There will also be an increase in implicit costs because the opportunity cost is larger for producing the items inside the United States (the items would be produced more efficiently overseas and for less of an opportunity cost). Overall, these costs lessen the profits from the clothing companies and hurt the economy in the clothing and textile sector (which has to do more macroeconomics).
These changes in explicit and implicit costs affect the overall profit of the company. Accounting profit (Total revenue - explicit costs) is much less after the tariffs are imposed because, provided that the total revenue stays constant or less than before, there are greater explicit costs, so the money earned (after paying off all of the costs) is less than it would be if it were produced overseas. The same goes for economic profit, however, the difference in economic profit would be greater than the difference in accounting profit for before and after the tariffs were imposed. This is because the implicit and explicit costs are both greater, so when calculating for the economic profit (Total revenue - explicit and implicit costs), there would be more subtracted from the total revenue, in turn making the economic profit much smaller. Furthermore, the profit of the companies will be closer to normal profit due to the difference in the total revenue and the total implicit and explicit costs being close to zero after the tariffs were put into place. When analyzing profit, the further away from the normal profit a company is (when the revenue is greater than costs), the better off the company is doing. Therefore, the companies producing clothing within the United States are less efficient when doing so, proving that the tariffs are not beneficial to the economy.
Marginal costs and revenues also vary when substantial tariffs are placed on a good. The marginal costs are greater after the tariffs are imposed because the cost added by producing one additional piece of clothing is larger (due to larger explicit costs). Also, provided that the total revenue would stay constant and the total quantity of goods would decrease, the marginal revenue would increase. Therefore, the quantity would be greater at the optimal output due to the fact that the marginal revenue and marginal cost are greater than before the tariffs were in place. In the end, even though the tariffs sound good at first, they end up hurting the clothing companies within the United States. The goal of imposing them is to try and get the clothing companies to produce clothing within our country, and it does so, only at the price of increased explicit/implicit costs, less overall revenue, and in turn less profit.

The table above represents countries in the European Union that the United States imported the most clothing from after the tariffs were imposed. Table from https://wits.worldbank.org
Written by: Nik D.
When looking on a smaller scale, these clothing tariffs can be devastating to clothing companies; in specific they affect implicit/explicit costs, profit, as well as the marginal cost/revenue of the companies. The production of the clothing being produced within the United States rather than overseas leads to greater explicit costs. A majority of the increased explicit costs are due to higher wages needed to pay to the workers in the United States. Yes, it is good that the businesses are producing product within our country, but then again they are doing so less efficiently than they would if the product was produced overseas. The increase in wages outweighs the costs of producing within the United States (such as less transportation cost due to no international transportation), so these tariffs are not beneficial whatsoever. The production of the clothing, as well as the material costs, are close to the exact same as they are overseas, so it is the increase in worker wages that is responsible for the greater explicit costs. There will also be an increase in implicit costs because the opportunity cost is larger for producing the items inside the United States (the items would be produced more efficiently overseas and for less of an opportunity cost). Overall, these costs lessen the profits from the clothing companies and hurt the economy in the clothing and textile sector (which has to do more macroeconomics).
These changes in explicit and implicit costs affect the overall profit of the company. Accounting profit (Total revenue - explicit costs) is much less after the tariffs are imposed because, provided that the total revenue stays constant or less than before, there are greater explicit costs, so the money earned (after paying off all of the costs) is less than it would be if it were produced overseas. The same goes for economic profit, however, the difference in economic profit would be greater than the difference in accounting profit for before and after the tariffs were imposed. This is because the implicit and explicit costs are both greater, so when calculating for the economic profit (Total revenue - explicit and implicit costs), there would be more subtracted from the total revenue, in turn making the economic profit much smaller. Furthermore, the profit of the companies will be closer to normal profit due to the difference in the total revenue and the total implicit and explicit costs being close to zero after the tariffs were put into place. When analyzing profit, the further away from the normal profit a company is (when the revenue is greater than costs), the better off the company is doing. Therefore, the companies producing clothing within the United States are less efficient when doing so, proving that the tariffs are not beneficial to the economy.
Marginal costs and revenues also vary when substantial tariffs are placed on a good. The marginal costs are greater after the tariffs are imposed because the cost added by producing one additional piece of clothing is larger (due to larger explicit costs). Also, provided that the total revenue would stay constant and the total quantity of goods would decrease, the marginal revenue would increase. Therefore, the quantity would be greater at the optimal output due to the fact that the marginal revenue and marginal cost are greater than before the tariffs were in place. In the end, even though the tariffs sound good at first, they end up hurting the clothing companies within the United States. The goal of imposing them is to try and get the clothing companies to produce clothing within our country, and it does so, only at the price of increased explicit/implicit costs, less overall revenue, and in turn less profit.
The table above represents countries in the European Union that the United States imported the most clothing from after the tariffs were imposed. Table from https://wits.worldbank.org
Wednesday, October 17, 2018
Hurricane Michael
Hurricane Michael:
Caleb Nordquist
Hurricane Michael destroyed the east coast this past month, where the death toll reached 18 people and several homes and stores were ravaged. The total cost of damages hasn’t concluded yet however currently they are between $1.5 billion and $3 billion however they could possibly reach around $4.5 billion of deficits. Another 500,000 policyholders in Florida were impacted by the savage storm and power was eliminated in the states from Florida all the way to West Virginia. Although the disaster destroyed several million lives, people believe that insurance companies are benefiting from the hurricane because of the sole fact that they are making money based off of destructed buildings and homes. The southeast corner of the USA was the targeted and afflicted states and the damages resemble that.

As far as most people know, the hurricane isn’t officially concluded. There are still high wind speeds and massive flooding that is ensuring that whatever was there before the hurricane isn’t there afterwards. According to Brock Long, administor of the FEMA, “We're still in life-safety mode. We're not even close to having discussions on rebuilding yet." (CBS News). So according to Brock, most people are still bracing for the wind and water while they see their houses and towns all around them being ravaged. While the hurricane is still occurring, the president has sent out search-and-rescue teams to all the states that were hit by the hurricane. Hurricane Michael also caused destruction to Mexico, when over 250 people were evacuated from their homes and cities because of how serious the threat was. Due to the damages and deaths, the hurricane has seriously hurt the poverty rating in the states. Now that recovery will occur, most buildings and companies are in bits and pieces, causing the jobs to go under and people to live without their careers. With only $4.5 billion dollars in damage, compared to last year’s deadly hurricanes (Irma and Harvey) which crippled the US economy with $180 billion of damages, Hurricane Michael didn’t take as much of an economic decline as past hurricanes have. That doesn’t separate the fact that millions of people are still out of the job for the time being.
Considering all of the damages and all of the hazards that are present in the environment, the damages are fatal and brutal. However, the country as a whole won’t be as affected economically speaking. The destruction is horrific and the damages are in the billions, however compared to prior natural disasters, Hurricane Michael hasn’t costed as much. So, from an economic standpoint, the hurricane caused severe damage and massive payments, however it’s a penny to pay compared to how much Hurricane Harvey and Katrina costed in the past.
Works Cited
CBS/AP. “Michael's Death Toll Jumps as Crews Search for Survivors - Live Updates.” CBS News, CBS Interactive, 12 Oct. 2018, www.cbsnews.com/live-news/hurricane-michael-damage-florida-flooding-georgia-power-outage-weather-deaths-today-live-updates/.
“Hurricane Michael Death Toll Climbs to 18; Trump to Visit Florida, Georgia.” The Weather Channel, weather.com/storms/hurricane/news/2018-10-15-hurricane-michael-latest-impacts-florida-georgia.
“The Damage Costs From Hurricane Michael Could Top $4.5 Billion.” Fortune, fortune.com/2018/10/11/hurricane-michael-damages/.
Caleb Nordquist
Hurricane Michael destroyed the east coast this past month, where the death toll reached 18 people and several homes and stores were ravaged. The total cost of damages hasn’t concluded yet however currently they are between $1.5 billion and $3 billion however they could possibly reach around $4.5 billion of deficits. Another 500,000 policyholders in Florida were impacted by the savage storm and power was eliminated in the states from Florida all the way to West Virginia. Although the disaster destroyed several million lives, people believe that insurance companies are benefiting from the hurricane because of the sole fact that they are making money based off of destructed buildings and homes. The southeast corner of the USA was the targeted and afflicted states and the damages resemble that.
As far as most people know, the hurricane isn’t officially concluded. There are still high wind speeds and massive flooding that is ensuring that whatever was there before the hurricane isn’t there afterwards. According to Brock Long, administor of the FEMA, “We're still in life-safety mode. We're not even close to having discussions on rebuilding yet." (CBS News). So according to Brock, most people are still bracing for the wind and water while they see their houses and towns all around them being ravaged. While the hurricane is still occurring, the president has sent out search-and-rescue teams to all the states that were hit by the hurricane. Hurricane Michael also caused destruction to Mexico, when over 250 people were evacuated from their homes and cities because of how serious the threat was. Due to the damages and deaths, the hurricane has seriously hurt the poverty rating in the states. Now that recovery will occur, most buildings and companies are in bits and pieces, causing the jobs to go under and people to live without their careers. With only $4.5 billion dollars in damage, compared to last year’s deadly hurricanes (Irma and Harvey) which crippled the US economy with $180 billion of damages, Hurricane Michael didn’t take as much of an economic decline as past hurricanes have. That doesn’t separate the fact that millions of people are still out of the job for the time being.
Considering all of the damages and all of the hazards that are present in the environment, the damages are fatal and brutal. However, the country as a whole won’t be as affected economically speaking. The destruction is horrific and the damages are in the billions, however compared to prior natural disasters, Hurricane Michael hasn’t costed as much. So, from an economic standpoint, the hurricane caused severe damage and massive payments, however it’s a penny to pay compared to how much Hurricane Harvey and Katrina costed in the past.
Works Cited
CBS/AP. “Michael's Death Toll Jumps as Crews Search for Survivors - Live Updates.” CBS News, CBS Interactive, 12 Oct. 2018, www.cbsnews.com/live-news/hurricane-michael-damage-florida-flooding-georgia-power-outage-weather-deaths-today-live-updates/.
“Hurricane Michael Death Toll Climbs to 18; Trump to Visit Florida, Georgia.” The Weather Channel, weather.com/storms/hurricane/news/2018-10-15-hurricane-michael-latest-impacts-florida-georgia.
“The Damage Costs From Hurricane Michael Could Top $4.5 Billion.” Fortune, fortune.com/2018/10/11/hurricane-michael-damages/.
Why Did Vine Die?
Why Did Vine Die?
Chloe Brossman
You all know the beloved vines that gave you hours of laughter. They created social norms and creative greetings that took over the world. Instead of saying hello to someone between classes, “hi welcome to Chili’s” was screamed across the hall. If vine was such an iconic app, why was it announced that it was going to shut down December 16th, 2016 and fully changed January 17th, 2017?

Initially, the goal for vine was supposed to be little 6 second clips about people’s daily life, snippets into a private world to then share with others. But even after the small test group, it became apparent that it wouldn’t stay like that. Users took a more creative approach, using it to create legendary videos that are viewed more than a billion times. Twitter had been running fine for some time before buying vine, they wanted to continue it and push it further but they didn’t take over their business, instead, left it to the original marketing team. The problem with that came about when Instagram released their 15-second video options. Some stars from Vine began to move to Instagram instead for the longer loop time. From there, Instagram then began to start promoting stars Instagrams by creating an “explore” tab which boosted people’s views. Vine fell behind, remaining under the 6-second barrier.

From there, stars began to demand that Vine compensate them for their videos like Instagram or other platforms do. Without much effort, Vine began tapping into their limited resources to pay people such as Logan Paul $200,000 for Vines. While people loved Vine, they were unable to keep up with the changing competitive social media sources. Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat all began to create a brand around them and advertise not only to people but on their site to gain money from companies. Together, these large social media’s took over the market with their increasingly unique add-ons and their celebrity base. Vine fell behind, unable to keep up in the highly competitive market.
Soon enough it was left to the core members and creators of Vines who stayed without much money from Vine. As the platform lost its money, Twitter took action, announcing that it will be shutting down the platform and instead it will be something that is attached to Twitter to create the videos.
The Vine fanbase was large, but as it went on, it shrunk, along with their influence in the market. Leaving no economic impact despite its social popularity. Now, you only are able to see existing relics of a past icon.
Works Cited
Newton, Casey. “Why Vine Died.” The Verge, The Verge, 28 Oct. 2016, www.theverge.com/2016/10/28/13456208/why-vine-died-twitter-shutdown.
Ng, Alfred. “Why Twitter Killed off Vine after a Short-Lived Run.” CNET, CNET, 27 Oct. 2016, www.cnet.com/news/twitter-kills-off-vine/.
Twitter (TWTR) will officially phase out its beloved six-second video service on Tuesday, and replace it with a "pared-down" camera application instead. “Twitter Officially Shuts down Vine.” CNNMoney, Cable News Network, money.cnn.com/2017/01/17/technology/vine-shuts-down/index.html.
Chloe Brossman
You all know the beloved vines that gave you hours of laughter. They created social norms and creative greetings that took over the world. Instead of saying hello to someone between classes, “hi welcome to Chili’s” was screamed across the hall. If vine was such an iconic app, why was it announced that it was going to shut down December 16th, 2016 and fully changed January 17th, 2017?
Initially, the goal for vine was supposed to be little 6 second clips about people’s daily life, snippets into a private world to then share with others. But even after the small test group, it became apparent that it wouldn’t stay like that. Users took a more creative approach, using it to create legendary videos that are viewed more than a billion times. Twitter had been running fine for some time before buying vine, they wanted to continue it and push it further but they didn’t take over their business, instead, left it to the original marketing team. The problem with that came about when Instagram released their 15-second video options. Some stars from Vine began to move to Instagram instead for the longer loop time. From there, Instagram then began to start promoting stars Instagrams by creating an “explore” tab which boosted people’s views. Vine fell behind, remaining under the 6-second barrier.
From there, stars began to demand that Vine compensate them for their videos like Instagram or other platforms do. Without much effort, Vine began tapping into their limited resources to pay people such as Logan Paul $200,000 for Vines. While people loved Vine, they were unable to keep up with the changing competitive social media sources. Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat all began to create a brand around them and advertise not only to people but on their site to gain money from companies. Together, these large social media’s took over the market with their increasingly unique add-ons and their celebrity base. Vine fell behind, unable to keep up in the highly competitive market.
Soon enough it was left to the core members and creators of Vines who stayed without much money from Vine. As the platform lost its money, Twitter took action, announcing that it will be shutting down the platform and instead it will be something that is attached to Twitter to create the videos.
The Vine fanbase was large, but as it went on, it shrunk, along with their influence in the market. Leaving no economic impact despite its social popularity. Now, you only are able to see existing relics of a past icon.
Works Cited
Newton, Casey. “Why Vine Died.” The Verge, The Verge, 28 Oct. 2016, www.theverge.com/2016/10/28/13456208/why-vine-died-twitter-shutdown.
Ng, Alfred. “Why Twitter Killed off Vine after a Short-Lived Run.” CNET, CNET, 27 Oct. 2016, www.cnet.com/news/twitter-kills-off-vine/.
Twitter (TWTR) will officially phase out its beloved six-second video service on Tuesday, and replace it with a "pared-down" camera application instead. “Twitter Officially Shuts down Vine.” CNNMoney, Cable News Network, money.cnn.com/2017/01/17/technology/vine-shuts-down/index.html.
Hurricane Michael
10/13/18
Ryan Novak
Economics A1
Mr. Reuter
Hurricane Michael
On October 10th, Hurricane Michael touched down on “Florida’s Panhandle”. This hurricane is a category 4 with wind speeds up to 155 mph. This hurricane has killed at least 8 in Florida and another 9 in other states like North Carolina, Virginia, and Georgia. This hurricane also completely massacred Mexico Beach, hitting it the hardest. People did not think the hurricane would be that devastating, the governor had required a mandatory evacuation and yet some did not leave. They definitely took a hit too from the pictures and information behind it saying how the houses had been completely ripped apart. Then the Staff Sgt. Andrew Pliscofsky said, “It was like a monster came through and kicked it all down. This all just shocked us.”. This was his fourth rescue mission and had never seen anything like it.

This photo is from Mexico Beach
Now, looking at the economics side of this, this hurricane had cost an estimated $25 billion. Around $3 million will be placed on the federal flood insurance program and then for the private insurances, they will be hit with around $9-10 billion. Money is not the only thing that was lost here, but also the power is obviously gone, no fuel, and sewage lines are also down. People have lost the homes that they have had for their entire life possible and if it is not gone, it is damaged severely.
Then, you must think about, “Where do these people go now or live?”. Well, there are many other states but they already have a lot of people and don’t another few thousand coming in all at once. If they go back to Florida, how are they supposed to live with no food, water, and home? The only way they’ll live is being on the side of the road or help from everybody or moving to a different state and getting a new job. But what about those with large families? As you can see there are many unanswered questions. First, flood insurance will help families get a couple thousand dollars to get back up. Secondly, helping shelters will have water for them most likely and not all of Florida was completely destroyed so they still have some food places/stores. Thirdly, the city hall is accepting people to live there and people have been living in there cars. Luckily this really only hit Mexico beach which is just a little community, so not many were affected.
After reading through many people’s stories from The New York Times. The average cost for evacuating was around $700 after like 3 days from out of pocket/credit card. Then they’ll have to go back and hope they still have a home and most likely be living off a generator if there is one. Then there is also a shortage in gas majorly. Florida took a devastating hit and will need all the help they can get to start living again and rebuilding. The estimated time to rebuild is around 1-2 years, so this will be awhile until they get better. Many of the people affected by this have never had anything like this, if you’ve seen on the TV how they ask for only $10, that goes a long way to giving food and water to those who need it and running generators for hospitals and living shelters. Just donate $10 and that’s all that’s asked of you.
Works Cited
Bloomberg.com, Bloomberg, www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-10-11/hurricane-michael-s-price-tag-could-reach-25-billion.
“'It's All Gone': Tiny Florida Beach Town Nearly Swept Away by Hurricane Michael.” The Washington Post, WP Company, 12 Oct. 2018, www.washingtonpost.com/national/its-all-gone-tiny-florida-beach-town-nearly-swept-away-by-hurricane-michael/2018/10/12/f1a110c0-ce56-11e8-a3e6-44daa3d35ede_story.html?noredirect=on&utm_term=.37294a922736.
Associated Press. “Hurricane Michael: Breaking down the Devastation Left in Florida, Elsewhere.” OrlandoSentinel.com, 12 Oct. 2018, www.orlandosentinel.com/weather/hurricane/os-ne-hurricane-michael-devastation-by-numbers-1012-story.html.
Chavez, Nicole. “Michael's Death Toll Rises to 17, Including 8 in Florida.” CNN, Cable News Network, 13 Oct. 2018, www.cnn.com/2018/10/12/us/hurricane-michael-wxc/index.html.
“Hurricane Michael May Have Disrupted Florida's Red Tide.” NBCNews.com, NBCUniversal News Group, www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/hurricane-michael-may-have-disrupted-florida-s-red-tide-n919826.
Moore, Lela. “The Price of Fleeing Hurricane Michael: 'We Are Going to Be Financially Devastated'.” The New York Times, The New York Times, 13 Oct. 2018, www.nytimes.com/2018/10/13/reader-center/evacuation-hurricane-michael.html.
Ryan Novak
Economics A1
Mr. Reuter
Hurricane Michael
On October 10th, Hurricane Michael touched down on “Florida’s Panhandle”. This hurricane is a category 4 with wind speeds up to 155 mph. This hurricane has killed at least 8 in Florida and another 9 in other states like North Carolina, Virginia, and Georgia. This hurricane also completely massacred Mexico Beach, hitting it the hardest. People did not think the hurricane would be that devastating, the governor had required a mandatory evacuation and yet some did not leave. They definitely took a hit too from the pictures and information behind it saying how the houses had been completely ripped apart. Then the Staff Sgt. Andrew Pliscofsky said, “It was like a monster came through and kicked it all down. This all just shocked us.”. This was his fourth rescue mission and had never seen anything like it.
This photo is from Mexico Beach
Now, looking at the economics side of this, this hurricane had cost an estimated $25 billion. Around $3 million will be placed on the federal flood insurance program and then for the private insurances, they will be hit with around $9-10 billion. Money is not the only thing that was lost here, but also the power is obviously gone, no fuel, and sewage lines are also down. People have lost the homes that they have had for their entire life possible and if it is not gone, it is damaged severely.
Then, you must think about, “Where do these people go now or live?”. Well, there are many other states but they already have a lot of people and don’t another few thousand coming in all at once. If they go back to Florida, how are they supposed to live with no food, water, and home? The only way they’ll live is being on the side of the road or help from everybody or moving to a different state and getting a new job. But what about those with large families? As you can see there are many unanswered questions. First, flood insurance will help families get a couple thousand dollars to get back up. Secondly, helping shelters will have water for them most likely and not all of Florida was completely destroyed so they still have some food places/stores. Thirdly, the city hall is accepting people to live there and people have been living in there cars. Luckily this really only hit Mexico beach which is just a little community, so not many were affected.
After reading through many people’s stories from The New York Times. The average cost for evacuating was around $700 after like 3 days from out of pocket/credit card. Then they’ll have to go back and hope they still have a home and most likely be living off a generator if there is one. Then there is also a shortage in gas majorly. Florida took a devastating hit and will need all the help they can get to start living again and rebuilding. The estimated time to rebuild is around 1-2 years, so this will be awhile until they get better. Many of the people affected by this have never had anything like this, if you’ve seen on the TV how they ask for only $10, that goes a long way to giving food and water to those who need it and running generators for hospitals and living shelters. Just donate $10 and that’s all that’s asked of you.
Works Cited
Bloomberg.com, Bloomberg, www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-10-11/hurricane-michael-s-price-tag-could-reach-25-billion.
“'It's All Gone': Tiny Florida Beach Town Nearly Swept Away by Hurricane Michael.” The Washington Post, WP Company, 12 Oct. 2018, www.washingtonpost.com/national/its-all-gone-tiny-florida-beach-town-nearly-swept-away-by-hurricane-michael/2018/10/12/f1a110c0-ce56-11e8-a3e6-44daa3d35ede_story.html?noredirect=on&utm_term=.37294a922736.
Associated Press. “Hurricane Michael: Breaking down the Devastation Left in Florida, Elsewhere.” OrlandoSentinel.com, 12 Oct. 2018, www.orlandosentinel.com/weather/hurricane/os-ne-hurricane-michael-devastation-by-numbers-1012-story.html.
Chavez, Nicole. “Michael's Death Toll Rises to 17, Including 8 in Florida.” CNN, Cable News Network, 13 Oct. 2018, www.cnn.com/2018/10/12/us/hurricane-michael-wxc/index.html.
“Hurricane Michael May Have Disrupted Florida's Red Tide.” NBCNews.com, NBCUniversal News Group, www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/hurricane-michael-may-have-disrupted-florida-s-red-tide-n919826.
Moore, Lela. “The Price of Fleeing Hurricane Michael: 'We Are Going to Be Financially Devastated'.” The New York Times, The New York Times, 13 Oct. 2018, www.nytimes.com/2018/10/13/reader-center/evacuation-hurricane-michael.html.
Wisconsin Pride
Wisconsin Pride
By:Jenna Brandl
To all the Badger fans out there, and yes that’s probably most of you reading this, but did you know that this last year or so for the 2017-2018 budget of Wisconsin Athletics was at a profound $132.4 million? I know, it’s shocking! At first I didn’t believe it either, but after reading an article on the Wisconsin State Journal webpage I found out where all of this money has gone too. It’s a mix of things really, $5.8 million of that $41.5 million in media rights revenue from the conference in the coming year will be going towards things such as sports medicine, psychology and academic services. The rest of that 97 percent will be going towards the growing student athletic programs. Though with all the new students and outstanding athletes coming into the school, they’ll need a place to stay that will be growing with these athletes throughout the coming years; that’s why about $10.9 million is being set aside for the campus.
Recently, I got the chance to go to the first UW Wisconsin Men’s Hockey game of the season this past Saturday (October 13th). After going I started to wonder just how much it would be for certain tickets for this one game not including the money from the 2017-2018 budget and if it was worth the amount of money for tickets. To start I found on the the UWBadgers website each of the tickets worth for each section and the amount of games provided. Here is what I found down below.
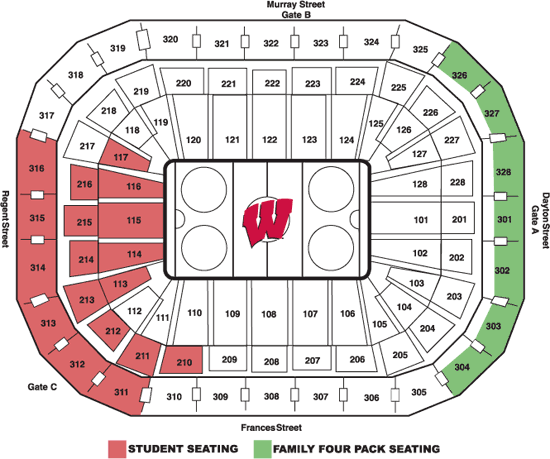
Group Ticket Levels (Single game)
Cost
15-39 tickets in the Reserved sections (100, 200, & 300 level)
$18.00
15-39 tickets in the Upper Reserved sections (row D and above in the 300 level)
$15.00
40 tickets in the Reserved sections (100, 200, & 300 level)
$13.00
40 tickets in the Upper Reserved sections (row D and above in the 300 level)
$11.00
Season Pass:
Face Off package→ $215, includes nine regular season home games, B1G quarterfinal 1, and the B1G semifinal.
Slap-Shot package → $230 Includes nine regular season home games, B1G quarterfinal 2 and 3, and the B1G Championship.
Contributions
Sections
$50 per seat sections
107, 108, 109, 121, 122, & 123
207, 209, 221, 222, & 223
$25 per seat sections
106, 110, 120, 124
Student Tickets:
Season Pass→ $115 + $20 Processing Fee
Sections: 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 211, 212, 213, 214, 215, 216, 311, 312, 313, 314, 315, & 316
After looking at these ticket prices a lot changed my thinking about how much these games actually cost. Are these ticket prices worth the games? For example what if you buy tickets and the team has a horrible game or gets crushed by their opponent. According to some ticket purchasers they don’t mind paying to watch the sport,for some students who have to pay alongside their college fees it may not sound like the best idea. This would be an example of an oppertunity cost for a student. They either get to go to the games and live the college life or they save that money for other goods and services like food, student funds, etc. If I was a student going to UW Madison there would be a very high chance of me paying for the season passes to really get to feel like a student at that school. Though I cannot say that about everyone’s decision on these tickets. According to another article on the Wisconsin Sate Journal the price of the UW Women’s Hockey team just got approved to increase the price of tickets, though many people think it won’t be worth the income in the long run. "Women's hockey already has the smallest sign board. It almost never has the band. We do get Bucky," said Viney, a law school professor. "But, otherwise, you're asking people to pay 30 or 60 percent more for their tickets, and they're all going to be asking me, 'What are we getting for that?'"(Wisconsin State Journal). In the end, it all depends on how committed of a Badger fan you are and how much you enjoy seeing them play by watching their games in person, which I certainly love to do.
Works Cited
“Men's Hockey - Ticket Information.” Men's Hockey - Ticket Information - Wisconsin Athletics, uwbadgers.com/sports/2015/8/21/GEN_20140101137.aspx.
Milewski, Todd D. “Badgers Sports: Committee Approves $132.4 Million Wisconsin Athletics Budget for 2017-18.” Madison.com, 9 Feb. 2017, madison.com/wsj/sports/college/badgers-sports-committee-approves-million-wisconsin-athletics-budget-for/article_985308d4-1752-5796-85a6-b4fcc28b087c.html.
Milewski, Todd D. “Committee Approves Wisconsin Badgers Women's Hockey Ticket Price Hike, OKs Wrestling Season Ticket Sales.” Madison.com, 17 May 2018, madison.com/wsj/sports/college/hockey/committee-approves-wisconsin-badgers-women-s-hockey-ticket-price-hike/article_585bedb2-df8a-5789-9add-069d5265683a.html.
Links:
https://madison.com/wsj/sports/college/badgers-sports-committee-approves-million-wisconsin-athletics-budget-for/article_985308d4-1752-5796-85a6-b4fcc28b087c.html
https://uwbadgers.com/sports/2015/8/21/GEN_20140101137.aspx
https://madison.com/wsj/sports/college/hockey/committee-approves-wisconsin-badgers-women-s-hockey-ticket-price-hike/article_585bedb2-df8a-5789-9add-069d5265683a.html
Image #1
Image #2
Companies are Working Against You
Elise Picard
Companies are working against you. No one reading this is a millionaire, no one reading this is a ceo, it’s safe to say you’re a worker or consumer in modern america, and I can tell you with a great deal of confidence that major businesses are working against you. Whether you’re middle class, lower class, or not sure of your place in the economy at the end of the day, we are being targeted in a variety of ways by corporations.
In america right now we live in late-stage capitalism. And in late-stage capitalism, gaining capital is the only thing that matters. From major businesses like Walmart for instance. In June of 2000 when meat workers decided to unionize in certain braches, unionize with no demands yet, Walmart ended the deli part of the store in six states, following with twenty states after that. The current CEO of walmart makes 22.8 million a year. Another example is ever popular Jeff Bezos. In a recent announcement Bezos claimed that he would be boosting the minimum wage of amazon workers to 15 dollars an hour. What he didn’t mention was the significant cuts to bonuses, forfeit of to a number of medical and dental plans, and commissions for white-collar workers. Jeff Bezos meanwhile has a net worth of 165 billion.
There’s a reason why companies are scared of unions, because their demands will ultimately draw capital away from the ceos and top managing class of workers. Their goal is not a safe or secure working environment, nor is it to pay workers a living wage. It’s too pay workers as little as possible for the maximum amount of gain. This is why, although you legally must offer breaks after working for a certain number of hours, many companies will schedule you for just under that requirement. Or companies will often berate and threaten workers, keeping them on the edge of passive exhaustion.
Companies aren’t just harming workers, they’re harming consumers too. Apple’s been a notorious perpetrator of rigging their products so that they can make the maximum amount of profit. When an apple product breaks, newer models now have a system that can detect if they’re being repaired. And the repairs, even if using official apple products, will lock the user out of the phone unless an official Apple code is entered certifying the repair is by the Apple company. Small tech repair businesses are suffering because a major corporation like Apple has put in place a firewall to ensure you have to pay a bigger price for a repair that could be completed by a local business. It harms small businesses, and it harms you the consumer.
And you may say ‘Then I’ll take my business elsewhere, I’ll buy my phone from a different company’. While that option is still available with phones, many other facets of business such as Internet provision is handled by only one or two providers. That’s why in many locations you don’t see competition. Businesses are no longer managed by small groups or local parties, many major brands are all owned by the same parent company.
These factors are obvious in our government as well. Many politicians, republican or democrat, have strong ties to corporations that manipulate their decisions. Corporate lobbyists have overtaken the government since the 70s, and their influence is unprecedented. One famous and recent example being chairperson of the FCC Ajit Pai who was noted to have ties to Sinclair Broadcasting. He then proposed and voted on changed Internet from Title II to Title I. This choice benefitting Sinclair Broadcasting. The writing was pretty on the wall or this one, but there are more subtle tactics of collusion with companies. Major tax cuts is one way, decreasing workplace regulation another, allowing companies to be treated like citizens is a hugely alarming one.
Corporations don’t just manipulate the government for their own benefit but manipulate the populus. A social media craze a few months ago was the Wendys twitter account, drawing on popular jokes and comedy to make you feel an attachment for the company. We don’t personify that company by it’s food or service, but rather by a faux persona created as a marketing tool to relate and manipulate young people. Corporations pretending to be people seems like an innocent marketing tactic, but is a subtly harmful as it makes corporations feel more human. A massive company should not be treated as a person, should not be treated with religious or personal rights. These social manipulation tactics make companies seem harmless and relatable, yet they are anything but.
Social manipulation is a tool that has been used by the government and corporations for years. In the case of corporations that often comes as punishing all workers for any union involvement, which often makes other workers dislike those who attempt to unionize, and perceive the union workers as the source of the misery, not the punishing company. This was evident in the meat handling union in Walmart. Now Walmart workers are too scared to unionize or else lose their job and get others fired. With the government this is another common manipulation. Often in the event of a disaster it’s the upper class appealing to the middle class to get them to donate to the lower class in disaster. Upper class members could just as easily donate, if not use their resources more effectively but often pull on the heartstrings of the middle class. Guilt tripping them into paying to help the lower class. Or in the instance of the most recent presidential election, instead of confronting the corerations and barriers keeping many people in poverty, the Trump campaign pitted one group of poor people against another group of poor people. Pitting lower class americans against immigrating mexican workers. Claiming the immigrants would steal their jobs and use up economic resources.
In America corporations have gotten out of hand, and similar to the industrial era are becoming more and more manipulative, more and more involved in the government, and more and more powerful. We talk about the degree of corruption in the industrial era and that corruption is a mirror image of what’s to come in American society. We need to regulate corporations, redistribute the wealth, and unionize. Politicians, Ceos, and Millionaires are working to preserve their wealth.
Works Cited
Ann ZimmermanStaff Reporter of The Wall Street Journal. “Pro-Union Butchers at Wal-Mart Win a Battle, but Lose the War.” The Wall Street Journal, Dow Jones & Company, 11 Apr. 2000, www.wsj.com/articles/SB955407680495911513.
CBS.MarketWatch.com. “Wal-Mart to Shut down Meat-Cutting Operations.” MarketWatch, MarketWatch, 4 Mar. 2000, www.marketwatch.com/story/wal-mart-to-shut-down-meat-cutting-operations.
“Corporate Personhood.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 20 July 2018, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corporate_personhood.
Feingold, Danny. “Walmart's War Against Unions -- and the U.S. Laws That Make It Possible.” The Huffington Post, TheHuffingtonPost.com, 5 Aug. 2013, www.huffingtonpost.com/julie-b-gutman/walmart-labor-laws_b_3390994.html.
Greenhouse, Steven. “How America's Largest Employer Persuades Its Workers Not to Unionize.” The Atlantic, Atlantic Media Company, 9 June 2015, www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2015/06/how-walmart-convinces-its-employees-not-to-unionize/395051/.
Harris, Ainsley. “Jeff Bezos Made 1.2 Million Times the Median Amazon Employee in 2017.” Fast Company, Fast Company, 23 Apr. 2018, www.fastcompany.com/40561786/jeff-bezos-made-1-2-million-times-the-median-amazon-employee-in-2017.
Norman, Al. “Wal-Mart's ‘Meat Wars’ With Union Sizzles On.” The Huffington Post, TheHuffingtonPost.com, 25 May 2011, www.huffingtonpost.com/al-norman/walmarts-meat-wars-with-u_b_91757.html.
Totenberg, Nina. “When Did Companies Become People? Excavating The Legal Evolution.” NPR, NPR, 28 July 2014, www.npr.org/2014/07/28/335288388/when-did-companies-become-people-excavating-the-legal-evolution.
Tuttle, Brad. “Jeff Bezos Net Worth 2018: Amazon CEO Has Made $40 Billion | Money.” Time, Time, 5 June 2018, time.com/money/5301812/jeff-bezos-net-worth-2018-amazon-worker-salary.
Winkler, Adam. “Corporations Are People, And They Have More Rights Than You.” The Huffington Post, TheHuffingtonPost.com, 30 Aug. 2014, www.huffingtonpost.com/adam-winkler/corporations-are-people-a_b_5543833.html.
facebook.com/jefferson.graham. “FCC Chair Ajit Pai Investigated for Sinclair Ties, Lawmakers Say.” USA Today, Gannett Satellite Information Network, 16 Feb. 2018, www.usatoday.com/story/tech/2018/02/15/fcc-chair-ajit-pai-investigated-sinclair-ties-lawmakers-say/342893002/.
Companies are working against you. No one reading this is a millionaire, no one reading this is a ceo, it’s safe to say you’re a worker or consumer in modern america, and I can tell you with a great deal of confidence that major businesses are working against you. Whether you’re middle class, lower class, or not sure of your place in the economy at the end of the day, we are being targeted in a variety of ways by corporations.
In america right now we live in late-stage capitalism. And in late-stage capitalism, gaining capital is the only thing that matters. From major businesses like Walmart for instance. In June of 2000 when meat workers decided to unionize in certain braches, unionize with no demands yet, Walmart ended the deli part of the store in six states, following with twenty states after that. The current CEO of walmart makes 22.8 million a year. Another example is ever popular Jeff Bezos. In a recent announcement Bezos claimed that he would be boosting the minimum wage of amazon workers to 15 dollars an hour. What he didn’t mention was the significant cuts to bonuses, forfeit of to a number of medical and dental plans, and commissions for white-collar workers. Jeff Bezos meanwhile has a net worth of 165 billion.
There’s a reason why companies are scared of unions, because their demands will ultimately draw capital away from the ceos and top managing class of workers. Their goal is not a safe or secure working environment, nor is it to pay workers a living wage. It’s too pay workers as little as possible for the maximum amount of gain. This is why, although you legally must offer breaks after working for a certain number of hours, many companies will schedule you for just under that requirement. Or companies will often berate and threaten workers, keeping them on the edge of passive exhaustion.
Companies aren’t just harming workers, they’re harming consumers too. Apple’s been a notorious perpetrator of rigging their products so that they can make the maximum amount of profit. When an apple product breaks, newer models now have a system that can detect if they’re being repaired. And the repairs, even if using official apple products, will lock the user out of the phone unless an official Apple code is entered certifying the repair is by the Apple company. Small tech repair businesses are suffering because a major corporation like Apple has put in place a firewall to ensure you have to pay a bigger price for a repair that could be completed by a local business. It harms small businesses, and it harms you the consumer.
And you may say ‘Then I’ll take my business elsewhere, I’ll buy my phone from a different company’. While that option is still available with phones, many other facets of business such as Internet provision is handled by only one or two providers. That’s why in many locations you don’t see competition. Businesses are no longer managed by small groups or local parties, many major brands are all owned by the same parent company.
These factors are obvious in our government as well. Many politicians, republican or democrat, have strong ties to corporations that manipulate their decisions. Corporate lobbyists have overtaken the government since the 70s, and their influence is unprecedented. One famous and recent example being chairperson of the FCC Ajit Pai who was noted to have ties to Sinclair Broadcasting. He then proposed and voted on changed Internet from Title II to Title I. This choice benefitting Sinclair Broadcasting. The writing was pretty on the wall or this one, but there are more subtle tactics of collusion with companies. Major tax cuts is one way, decreasing workplace regulation another, allowing companies to be treated like citizens is a hugely alarming one.
Corporations don’t just manipulate the government for their own benefit but manipulate the populus. A social media craze a few months ago was the Wendys twitter account, drawing on popular jokes and comedy to make you feel an attachment for the company. We don’t personify that company by it’s food or service, but rather by a faux persona created as a marketing tool to relate and manipulate young people. Corporations pretending to be people seems like an innocent marketing tactic, but is a subtly harmful as it makes corporations feel more human. A massive company should not be treated as a person, should not be treated with religious or personal rights. These social manipulation tactics make companies seem harmless and relatable, yet they are anything but.
Social manipulation is a tool that has been used by the government and corporations for years. In the case of corporations that often comes as punishing all workers for any union involvement, which often makes other workers dislike those who attempt to unionize, and perceive the union workers as the source of the misery, not the punishing company. This was evident in the meat handling union in Walmart. Now Walmart workers are too scared to unionize or else lose their job and get others fired. With the government this is another common manipulation. Often in the event of a disaster it’s the upper class appealing to the middle class to get them to donate to the lower class in disaster. Upper class members could just as easily donate, if not use their resources more effectively but often pull on the heartstrings of the middle class. Guilt tripping them into paying to help the lower class. Or in the instance of the most recent presidential election, instead of confronting the corerations and barriers keeping many people in poverty, the Trump campaign pitted one group of poor people against another group of poor people. Pitting lower class americans against immigrating mexican workers. Claiming the immigrants would steal their jobs and use up economic resources.
In America corporations have gotten out of hand, and similar to the industrial era are becoming more and more manipulative, more and more involved in the government, and more and more powerful. We talk about the degree of corruption in the industrial era and that corruption is a mirror image of what’s to come in American society. We need to regulate corporations, redistribute the wealth, and unionize. Politicians, Ceos, and Millionaires are working to preserve their wealth.
Works Cited
Ann ZimmermanStaff Reporter of The Wall Street Journal. “Pro-Union Butchers at Wal-Mart Win a Battle, but Lose the War.” The Wall Street Journal, Dow Jones & Company, 11 Apr. 2000, www.wsj.com/articles/SB955407680495911513.
CBS.MarketWatch.com. “Wal-Mart to Shut down Meat-Cutting Operations.” MarketWatch, MarketWatch, 4 Mar. 2000, www.marketwatch.com/story/wal-mart-to-shut-down-meat-cutting-operations.
“Corporate Personhood.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 20 July 2018, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corporate_personhood.
Feingold, Danny. “Walmart's War Against Unions -- and the U.S. Laws That Make It Possible.” The Huffington Post, TheHuffingtonPost.com, 5 Aug. 2013, www.huffingtonpost.com/julie-b-gutman/walmart-labor-laws_b_3390994.html.
Greenhouse, Steven. “How America's Largest Employer Persuades Its Workers Not to Unionize.” The Atlantic, Atlantic Media Company, 9 June 2015, www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2015/06/how-walmart-convinces-its-employees-not-to-unionize/395051/.
Harris, Ainsley. “Jeff Bezos Made 1.2 Million Times the Median Amazon Employee in 2017.” Fast Company, Fast Company, 23 Apr. 2018, www.fastcompany.com/40561786/jeff-bezos-made-1-2-million-times-the-median-amazon-employee-in-2017.
Norman, Al. “Wal-Mart's ‘Meat Wars’ With Union Sizzles On.” The Huffington Post, TheHuffingtonPost.com, 25 May 2011, www.huffingtonpost.com/al-norman/walmarts-meat-wars-with-u_b_91757.html.
Totenberg, Nina. “When Did Companies Become People? Excavating The Legal Evolution.” NPR, NPR, 28 July 2014, www.npr.org/2014/07/28/335288388/when-did-companies-become-people-excavating-the-legal-evolution.
Tuttle, Brad. “Jeff Bezos Net Worth 2018: Amazon CEO Has Made $40 Billion | Money.” Time, Time, 5 June 2018, time.com/money/5301812/jeff-bezos-net-worth-2018-amazon-worker-salary.
Winkler, Adam. “Corporations Are People, And They Have More Rights Than You.” The Huffington Post, TheHuffingtonPost.com, 30 Aug. 2014, www.huffingtonpost.com/adam-winkler/corporations-are-people-a_b_5543833.html.
facebook.com/jefferson.graham. “FCC Chair Ajit Pai Investigated for Sinclair Ties, Lawmakers Say.” USA Today, Gannett Satellite Information Network, 16 Feb. 2018, www.usatoday.com/story/tech/2018/02/15/fcc-chair-ajit-pai-investigated-sinclair-ties-lawmakers-say/342893002/.
Tuesday, October 16, 2018
Kylie Jenner and the economics of her lip kits.
Kylie Jenner and the economics of her lip kits.
Swati Dalmia
 The youngest of the Jenner/Kardashian siblings, Kylie Jenner is a reality TV personality turned businesswoman. With her networth of about $900 million, she is on track to becoming the youngest billionaire in the world. Taking advantage of the plump lips that contributed to her rise to fame, Kylie Jenner launched her own cosmetics line called Kylie Cosmetics in 2015. But what was the reason for Kylie’s immense success? What was so special about her lip kits that made them sell out instantaneously and made her one of the richest teenagers in the world? Jenner’s strategic business plan that utilizes the concepts of scarcity and demand was a key element that helped her become an icon in the makeup industry.
The youngest of the Jenner/Kardashian siblings, Kylie Jenner is a reality TV personality turned businesswoman. With her networth of about $900 million, she is on track to becoming the youngest billionaire in the world. Taking advantage of the plump lips that contributed to her rise to fame, Kylie Jenner launched her own cosmetics line called Kylie Cosmetics in 2015. But what was the reason for Kylie’s immense success? What was so special about her lip kits that made them sell out instantaneously and made her one of the richest teenagers in the world? Jenner’s strategic business plan that utilizes the concepts of scarcity and demand was a key element that helped her become an icon in the makeup industry.
When the first three shades of Kylie Jenner’s lip kits were released, they sold out after a single minute due to high demand. With a new change in the taste of consumers (women wanting their lips to look fuller), the demand of her products drastically increased, causing subsequent releases of additional colours to be sold out in less than ten minutes. Despite retailing at $29, the lip kits became a unique phenomenon in the makeup industry for often being resold on eBay at a huge mark-up price, with bids on lip kits going as high as $10,000. This is because the lip kits identify as a status item and an item of scarcity. The high premium that consumers pay for Kylie Cosmetics is attributed to its scarcity in the market, the status that comes along with it, and the high number of beauty gurus and teenagers as consumers.
 The selling out of new Kylie Cosmetics products in minutes after a release or restock is a classic example of demand exceeding supply. For marketing reasons, Kylie Cosmetics may be selling limited quantities of their products to create a frenzy around the brand. The buzz generated by the hyped brand can create more interest to consumers in the long-term and lead to higher demand. The difficulty of acquiring a lip kit cements its recognition as a status item. By creating scarcity in the market, Kylie Cosmetics is therefore able to make the brand seem more valuable. The demand for her lip kits increases due to determinants such as change in taste, change in expectations for the future and change in the number of consumers in the market.
The selling out of new Kylie Cosmetics products in minutes after a release or restock is a classic example of demand exceeding supply. For marketing reasons, Kylie Cosmetics may be selling limited quantities of their products to create a frenzy around the brand. The buzz generated by the hyped brand can create more interest to consumers in the long-term and lead to higher demand. The difficulty of acquiring a lip kit cements its recognition as a status item. By creating scarcity in the market, Kylie Cosmetics is therefore able to make the brand seem more valuable. The demand for her lip kits increases due to determinants such as change in taste, change in expectations for the future and change in the number of consumers in the market.
While speed is the key factor which allocates the lip kits in the primary market, in the secondary market, the goods are solely allocated by consumers’ willingness to pay. Many resellers bulk order in the primary market with the intent to price discriminate for profit on the secondary market. Due to scarcity, independent resellers can sell at exorbitant prices on the secondary market. Although resellers profit from taking up more consumer surplus, they may create value by providing product availability in the late market and provide a means for those who are willing to pay more to get the product.
A significant part of the lipstick’s value comes from Kylie Jenner’s celebrity status and the endorsement of her well-known siblings. Beauty gurus and teenagers have preferences for Kylie Jenner’s products because she is a celebrity known for her full lips. There are many substitutes on the market for a matte lipstick with similar formulas, colours and quality. For instance, the products of Kylie Cosmetics and its sister company ColourPop are made by the same manufacturer. Many beauty bloggers claim that ColourPop’s Ultra Matte Lip liquid lipsticks are the inexpensive replicas of the Kylie Lip Kits at a cost of $6 per lipstick. If ColourPop and Kylie have the same manufacturing costs, the $25 price differential between the two company’s matte lipsticks can be attributed to Kylie Jenner’s brand. Avid fans are often willing to pay premiums for products they associate with their favourite figures in entertainment. For this reason, sneaker enthusiasts paid up to $1000 on Kanye West’s limited edition Yeezy Boost sneakers which retailed for $315.
In conclusion, it is apparent from the Kylie Cosmetics craze that there has been a strong desire in the marketplace for full lips like Kylie Jenner. The brand’s success is a result of Jenner using the concept of scarcity and the law of demand in her business. Despite the public’s mixed feelings towards Kylie Jenner, there is no doubt that she’s a great opportunist who has fuelled and capitalised on the need for a plump pout.
Erdogan, Melodi. “Kylie Jenner’s Lip Kits Are On eBay For Waaay More Then The Original Price.” Bustle, 1 Dec. 2015, https://www.bustle.com/articles/126850-kylie-jenners-lip-kits- are-on-ebay-for-waaay-more-then-the-original-price.
Homes, Sally. “Kylie Jenner’s Lip Kits sold out in less than a minute.” Elle, 30 Nov. 2015, https://www.elle.com/beauty/makeup-skin-care/news/a32225/kylie-jenners-lip-kit-sold-out-in-less-than-a-minute/.
Robehmen, Natalie. “How 20-Year-Old Kylie Jenner Built A $900 Million Fortune In Less Than 3 Years.” Forbes, 11 Jul. 2018,https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesdigitalco vers/2018/07/11/how-20-year-old-kylie-jenner-built-a-900-million-fortune-in-less-than-3-years/.
Swati Dalmia
When the first three shades of Kylie Jenner’s lip kits were released, they sold out after a single minute due to high demand. With a new change in the taste of consumers (women wanting their lips to look fuller), the demand of her products drastically increased, causing subsequent releases of additional colours to be sold out in less than ten minutes. Despite retailing at $29, the lip kits became a unique phenomenon in the makeup industry for often being resold on eBay at a huge mark-up price, with bids on lip kits going as high as $10,000. This is because the lip kits identify as a status item and an item of scarcity. The high premium that consumers pay for Kylie Cosmetics is attributed to its scarcity in the market, the status that comes along with it, and the high number of beauty gurus and teenagers as consumers.
While speed is the key factor which allocates the lip kits in the primary market, in the secondary market, the goods are solely allocated by consumers’ willingness to pay. Many resellers bulk order in the primary market with the intent to price discriminate for profit on the secondary market. Due to scarcity, independent resellers can sell at exorbitant prices on the secondary market. Although resellers profit from taking up more consumer surplus, they may create value by providing product availability in the late market and provide a means for those who are willing to pay more to get the product.
A significant part of the lipstick’s value comes from Kylie Jenner’s celebrity status and the endorsement of her well-known siblings. Beauty gurus and teenagers have preferences for Kylie Jenner’s products because she is a celebrity known for her full lips. There are many substitutes on the market for a matte lipstick with similar formulas, colours and quality. For instance, the products of Kylie Cosmetics and its sister company ColourPop are made by the same manufacturer. Many beauty bloggers claim that ColourPop’s Ultra Matte Lip liquid lipsticks are the inexpensive replicas of the Kylie Lip Kits at a cost of $6 per lipstick. If ColourPop and Kylie have the same manufacturing costs, the $25 price differential between the two company’s matte lipsticks can be attributed to Kylie Jenner’s brand. Avid fans are often willing to pay premiums for products they associate with their favourite figures in entertainment. For this reason, sneaker enthusiasts paid up to $1000 on Kanye West’s limited edition Yeezy Boost sneakers which retailed for $315.
In conclusion, it is apparent from the Kylie Cosmetics craze that there has been a strong desire in the marketplace for full lips like Kylie Jenner. The brand’s success is a result of Jenner using the concept of scarcity and the law of demand in her business. Despite the public’s mixed feelings towards Kylie Jenner, there is no doubt that she’s a great opportunist who has fuelled and capitalised on the need for a plump pout.
Work Cited
Canal, Emily. “Kylie Jenner’s lip kits, social status and the economics of scarcity.” Forbes, 2 Mar. 2016, https://www.forbes.com/sites/emilycanal/2016/03/02/kylie-jenners-li p-kits-social-status-and-the-economics-of-scarcity/#62c41b412960.Erdogan, Melodi. “Kylie Jenner’s Lip Kits Are On eBay For Waaay More Then The Original Price.” Bustle, 1 Dec. 2015, https://www.bustle.com/articles/126850-kylie-jenners-lip-kits- are-on-ebay-for-waaay-more-then-the-original-price.
Homes, Sally. “Kylie Jenner’s Lip Kits sold out in less than a minute.” Elle, 30 Nov. 2015, https://www.elle.com/beauty/makeup-skin-care/news/a32225/kylie-jenners-lip-kit-sold-out-in-less-than-a-minute/.
Robehmen, Natalie. “How 20-Year-Old Kylie Jenner Built A $900 Million Fortune In Less Than 3 Years.” Forbes, 11 Jul. 2018,https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesdigitalco vers/2018/07/11/how-20-year-old-kylie-jenner-built-a-900-million-fortune-in-less-than-3-years/.
Thursday, October 11, 2018
Hurricane Florence
Luke Lochner
Hurricane Florence devastated the East coast, particularly South Carolina, North Carolina, and Maryland in September of 2018. It hit land on August 31st, 2018 and the storm and resulting flooding lasted until the 19th of September. Storms similar to this, such as Hurricane Harvey, which hit Houston in 2017, and Hurricane Irma, which hit the West coast of Florida in 2017, greatly impact the nation’s economy due to the high cost of repairing and rebuilding damaged homes and buildings, death and destruction to livestock and farm land, and the temporary shut down of businesses in the aftermath of the storm. Ultimately, some businesses benefit from the hurricane, such as, insurance and finance companies and for disaster recovery, including, North Star Group Services.

The estimated total cost to repair damages from Florence is $17-$22 billion dollars and this number could increase (Domm). This includes housing, schools, and other buildings. Based on the visual, we can tell that this cost is far less than those of past devastating hurricanes. Fortunately, the 2 major ports in the Carolinas were not significantly damaged. The Port of Charleston is significant for the US economy as a cruise ship destination and because it handles a large amount of motor vehicle imports and exports. In 2015, the Port of Charleston ranked as the 6th port in the United States by cargo value, with $75 billion in imports and exports traded across the docks so it is important to the US economy to keep it fully functioning (Port). According to Zandi, the author of this article, he predicts that there will be, “about a 0.2 percentage point hit to GDP,” (Domm). This is only about half the impact that Hurricane Harvey had on Houston and 1/6 of the impact that Hurricane Irma had on Florida.
Due to the amount of damage Hurricane Florence inflicted on the east coast there will be an abundance of job opportunities in construction and for retailers that sell buildings and supplies (Wiseman). This will aid the US economy because it will potentially reduce the amount of unemployment and reduce the amount of poverty in the US. This will also boost the profits in those retailing businesses.

Some of the companies in the area handled waste of animals, “including toxic animal waste containment sites, which sent bacteria and hazardous chemicals into the water,” (Irfan). All the bacteria and hazardous chemicals need to be cleaned up in some way and that will cost money. Not only will costs need to be utilized in rebuilding and fixing up damaged buildings, it will be needed to clean up the streets of materials from those houses and buildings but also the chemicals and bacteria that is in the flood waters.
Overall, this hurricane will not have as large of an effect on the US economy as past hurricanes have. “Hurricanes Harvey (in Texas) and Irma (in Florida) last year sliced U.S. economic growth in the third quarter by about a half-percentage point. And the storms caused a whopping $180 billion in damage.” Compare this to Hurricane Florence which is projected to, “shave economic growth in the current quarter by one- to two-tenths of a percentage point,” (Davidson) and we can see by the data that the two hurricanes last year took a much greater toll on the economy than Florence will.
Ultimately, the costs and the effect on the economy are not the most important thing when it comes to natural disasters. The most important data points are the number of lives lost and people affected. The numbers are important when it comes to rebuilding those people’s lives and giving them comfort and support through the process.
Works Cited
Davidson, Paul. “Hurricane Florence, despite Destruction, Will Likely Have Small Impact on US Economy.” USA Today, Gannett Satellite Information Network, 18 Sept. 2018.
Domm, Patti. “Hurricane Florence Damage Estimated at $17 Billion to $22 Billion - Moody's Analytics.” CNBC, CNBC, 17 Sept. 2018.
Irfan, Umair. “Hurricane Florence Caused up to $22 Billion in Damages. Climate Change Made the Storm Worse.” Vox, Vox, 3 Oct. 2018.
“Port of Charleston.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 30 Apr. 2018.
Wiseman, Paul. “Businesses Are Bracing for Hurricane Florence. Here's How It Will Effect Costal Economies.” Inc.com, Inc., 13 Sept. 2018.
Hurricane Florence devastated the East coast, particularly South Carolina, North Carolina, and Maryland in September of 2018. It hit land on August 31st, 2018 and the storm and resulting flooding lasted until the 19th of September. Storms similar to this, such as Hurricane Harvey, which hit Houston in 2017, and Hurricane Irma, which hit the West coast of Florida in 2017, greatly impact the nation’s economy due to the high cost of repairing and rebuilding damaged homes and buildings, death and destruction to livestock and farm land, and the temporary shut down of businesses in the aftermath of the storm. Ultimately, some businesses benefit from the hurricane, such as, insurance and finance companies and for disaster recovery, including, North Star Group Services.
The estimated total cost to repair damages from Florence is $17-$22 billion dollars and this number could increase (Domm). This includes housing, schools, and other buildings. Based on the visual, we can tell that this cost is far less than those of past devastating hurricanes. Fortunately, the 2 major ports in the Carolinas were not significantly damaged. The Port of Charleston is significant for the US economy as a cruise ship destination and because it handles a large amount of motor vehicle imports and exports. In 2015, the Port of Charleston ranked as the 6th port in the United States by cargo value, with $75 billion in imports and exports traded across the docks so it is important to the US economy to keep it fully functioning (Port). According to Zandi, the author of this article, he predicts that there will be, “about a 0.2 percentage point hit to GDP,” (Domm). This is only about half the impact that Hurricane Harvey had on Houston and 1/6 of the impact that Hurricane Irma had on Florida.
Due to the amount of damage Hurricane Florence inflicted on the east coast there will be an abundance of job opportunities in construction and for retailers that sell buildings and supplies (Wiseman). This will aid the US economy because it will potentially reduce the amount of unemployment and reduce the amount of poverty in the US. This will also boost the profits in those retailing businesses.
Some of the companies in the area handled waste of animals, “including toxic animal waste containment sites, which sent bacteria and hazardous chemicals into the water,” (Irfan). All the bacteria and hazardous chemicals need to be cleaned up in some way and that will cost money. Not only will costs need to be utilized in rebuilding and fixing up damaged buildings, it will be needed to clean up the streets of materials from those houses and buildings but also the chemicals and bacteria that is in the flood waters.
Overall, this hurricane will not have as large of an effect on the US economy as past hurricanes have. “Hurricanes Harvey (in Texas) and Irma (in Florida) last year sliced U.S. economic growth in the third quarter by about a half-percentage point. And the storms caused a whopping $180 billion in damage.” Compare this to Hurricane Florence which is projected to, “shave economic growth in the current quarter by one- to two-tenths of a percentage point,” (Davidson) and we can see by the data that the two hurricanes last year took a much greater toll on the economy than Florence will.
Ultimately, the costs and the effect on the economy are not the most important thing when it comes to natural disasters. The most important data points are the number of lives lost and people affected. The numbers are important when it comes to rebuilding those people’s lives and giving them comfort and support through the process.
Works Cited
Davidson, Paul. “Hurricane Florence, despite Destruction, Will Likely Have Small Impact on US Economy.” USA Today, Gannett Satellite Information Network, 18 Sept. 2018.
Domm, Patti. “Hurricane Florence Damage Estimated at $17 Billion to $22 Billion - Moody's Analytics.” CNBC, CNBC, 17 Sept. 2018.
Irfan, Umair. “Hurricane Florence Caused up to $22 Billion in Damages. Climate Change Made the Storm Worse.” Vox, Vox, 3 Oct. 2018.
“Port of Charleston.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 30 Apr. 2018.
Wiseman, Paul. “Businesses Are Bracing for Hurricane Florence. Here's How It Will Effect Costal Economies.” Inc.com, Inc., 13 Sept. 2018.
Stock Market Returns Effected by Real World Events
Anthony Desidero
In the summer of 2015, tens of thousands of gamers flocked to an airtight dome in the middle of LA for an annual conference called E3. It was the hottest gaming event of the year, with multiple announcements and reveals from major game companies. But one unveiling had an unintended by-product. As Square Enix finished off their press conference, they announced one final project; a remake of the critically acclaimed game “Final Fantasy VII.” Almost instantly after this announcement, this happened:
That is a raise of nearly 3% in under an hour. Now there isn’t really an average stat for measuring market return value because the stock market fluctuates so much, but in order for a company’s stocks to suddenly surge to their highest levels since 2008, something major had to have happened. The same goes for any other market or company. In irder to hit umkbers like this, something good (or bad) had to have happened. This leads to to the point of this discussion: Stock market fluctuations depend solely on the supply/demand curve of that company, and the amount of bad/good PR it has.
Take, for instance BP. Their overall stock shares were fine through the 2010 year, until an oversight of basic safety procedures allowed the Gulf Oil Spill in April of that year, resulting in the largest oil spill recorded in history. Over the course of 60 days, BP’s stocks dropped 48%.
Both supply and PR are the cause of this here. The terrible press of being associated with the worst oil spill ever, having to clean up the damage, and the natural ramifications would deter investors quickly. Along with this, the supply of oil dropped significantly, and consumers are more likely to get their oil from different places, due to the PR the company received. This caused a massive withdrawal of stocks, as the stockbrokers (or rather, robots that manage and trade stocks for other humans) quickly sold what they could for as much profit as possible. But does any of this matter? Do companies really care about how much or little their stocks go for? Do they even affect the company at all?
Well...Yes and no. If I buy a share of BP for $60 and sell it for $20, then I’ve lost $40, not the company. Stock selling and management is a whole nother field in itself. But at the same time, a company that lives on its public identity will die by it. The Lehman banks went from riches to rags due to their stocks crashing completely during the 2008 calamity. It all depends on how much a company lives by its self image, and by how much stockbrokers and consumers pay attention to them.
At the end of the day, the stock market is a crazy, volatile slot machine in disguise as something professional. You sit down at the table, and there are countless bets you can place. Which one is the right one? The only way to tell is by doing the hardest thing of all: Waiting.
Works Cited
“BP Shares Recover after Reassurance.” CNNMoney, Cable News Network, money.cnn.com/2010/06/10/news/companies/BP_stock/index.htm.
Burke, Jackson. “Final Fantasy VII Remake Boosts Square Enix Stock.” CNBC, CNBC, 17 June 2015, www.cnbc.com/2015/06/17/sy-vii-remake-boosts-square-enix-stock-to-highest-level-2008.html.
Palmer, Brian. “Does It Matter to a Company If Its Stocks Lose Value?” Slate Magazine, Slate, 9 Aug. 2011, slate.com/news-and-politics/2011/08/does-it-matter-to-a-company-if-its-stocks-lose-value.html.
Is Amazon a Monopoly?
Written by: Stephanie Varin
Is Amazon a Monopoly?
The growth of the Amazon, the e-commerce company, is staggering. Year over year, they have consistently grown by $15 billion dollars, according to to CNBC. It’s growth has been enormous within the past few years as it has absorbed many companies from several different industries. This worries economists and politicians across the board, including POTUS, Donald Trump. In fact, if Trump is reelected, it is very possible he will appeal to the Senate in order to create new antitrust laws that might force Amazon to break up. Why all the fuss? Many believe that Amazon is quickly becoming too big and too powerful. In short, Amazon may be becoming a monopoly.
So, is Amazon becoming a monopoly? Well, no. Though some believe the company is becoming the textbook definition of a controlling power in the market, as least for our standards, it isn’t. According the Merriam-Webster, “a monopoly occurs when complete control of the entire supply of goods or of a service in a certain area or market rests with a single entity,”, and the FTC defines a monopoly as a company with +50% total market share, whereas Amazon only controls 5% of all retail sale in the US (Forbes). However, it does exhibit some monopolistic tendencies (see this video for a summary). For example, about 1 in every 2 dollars spent online is spent at Amazon. Also, in 2016, Amazon’s sales were six times greater than the online sales of Walmart, Target, Best Buy, Nordstrom, Home Depot, Macy’s, and Costco, combined (HowStuffWorks). Not only this, but Amazon seems to be dipping its toe into every pond out there, and has significant market value in many industries, including, but not limited to, electronics retail, fashion, consumable manufacturing, food delivery, grocery, bookstores, healthcare, pharmacy, and web services (CNBC). With all of its market holdings, Amazon is making many companies within these industries very nervous, and could very well threaten their performance, especially that of brick and mortar stores. So why isn’t the FTC taking action against this retail giant? Well, it’s all based in the consumer welfare. Because Amazon’s prices are so low, one of the many reasons that consumers love the site, it can’t be seen as threatening the consumers, and thus some economists don’t see it as a problem (Forbes). Also, it isn’t restricting trade which is the largest reason why monopolies are restricted and banned -- government wants to promote competitive and free trade.
So, is Amazon a monopoly by traditionally defined standards? No, but that does not mean that Congress could not create new antitrust laws that redefine what a monopoly is, and if that happens, Amazon could be in deep trouble.
Works Cited
Hanbury, Kate Taylor Mary. “Amazon's Growth Could Threaten These 10 Industries.” Business Insider, Business Insider, 28 June 2018, www.businessinsider.com/amazon-is-killing-these-7-companies-2017-7#healthcare-companies-8.
Ladd, Brittain. “Is Amazon A Monopoly? Donald Trump Thinks So.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 30 July 2018, www.forbes.com/sites/brittainladd/2018/07/29/amazon-is-not-a-monopoly-president-trump-yet/#46aa580c4735.
Markets, Economy &. “Here's Why Amazon Isn't a Monopoly.” Business Insider, Business Insider, 15 Aug. 2017, www.businessinsider.com/amazon-stock-price-not-a-monopoly-2017-8.
Salinas, Sara. “Amazon Sales Grew by $15 Billion Year over Year - Its Peers Don't Come Close to That Level of Growth.” CNBC, CNBC, 27 July 2018, www.cnbc.com/2018/07/27/amazon-sales-grew-by-15-billion-year-over-year-blowing-away-peers.html.
“Why Is Amazon Not Considered a Monopoly?” HowStuffWorks, HowStuffWorks, 11 Dec. 2017, money.howstuffworks.com/why-is-amazon-not-considered-monopoly.htm.
Thursday, October 4, 2018
Sea Turtles, Straw and the Economy: How does this affect you?
Sea Turtles, Straws, and the Economy: How Does This Affect You?
Maddie Pieper
Starbucks, an internationally and insanely popular coffee chain, announced to globally eliminate plastic straws from all of their locations by 2020. This announcement is in regards to the overwhelming amount of plastic in our ocean, and how it’s killing at least 100 million marine animals annually. So much plastic is dumped into our oceans, killing 700 species of animals. While Starbucks’ promise to ban plastic straws form their facilities won’t solely fix the problem, it will help decrease the amount of plastic in our oceans.

However, the cost of saving our ocean ecosystem is the price of the straw manufacturers. By converting to no straws, nearly 2,000 jobs would be lost in New York City, 8,000 in California, and 400 million dollars in economic activity. If no one is ordering plastic straws, the manufacturers will go out of business. Banning plastic straws sounds like a great plan when thinking short term, but long term, could it do more harm than good? The California State Water Resources Control Board released a study that said, “mere substitution would not result in reduced trash generation if such product substitution would be discarded in the same manner as the banned item” (The Daily Wire). Even though reusable straws are environmentally more friendly, if we continually dispose of them as we did prior to the ban, our oceans will still be affected by the waste. The table below shows the cost and effects of banning plastic straws in New York City alone. In total, it would cost approximately 91.3 million dollars to eliminate plastic straws from only one city.

See link here to table here for more information
The plastic straw ban has been controversial for years now, regaining popularity in the news due to Starbucks’ promise (Starbucks Newsroom). Plastic straws are something so ordinary and a part of our everyday culture, many wouldn’t think have how big of an impact they have on our earth and our economy. Are the jobs lost worth the reduction of the trash in the ocean, or will skipping the straw help us more in the long run?
Works Cited
Lockhart, Keely. “Plastic Straw Removed from Turtle's Nose by Marine Biologists in Heartbreaking Video .” The Telegraph, Telegraph Media Group, 22 Mar. 2016, www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2016/03/22/plastic-straw-removed-from-turtles-nose-by-marine-biologists-in/.
“Plastikmüll Im Meer.” Syrdallschoulen, portal.education.lu/syrdallschoulen/KIDS/News-fir-Kids/ArtMID/4828/ArticleID/560209/Plastikm252ll-im-Meer.
“Starbucks to Eliminate Plastic Straws Globally by 2020.” Starbucks Newsroom, 9 July 2018, news.starbucks.com/press-releases/starbucks-to-eliminate-plastic-straws-globally-by-2020.
“These 5 Marine Animals Are Dying Because of Our Plastic Trash ... Here's How We Can Help.” One Green Planet, 5 Feb. 2017, www.onegreenplanet.org/animalsandnature/marine-animals-are-dying-because-of-our-plastic-trash/.
“Http://Www.ijaerd.com/Papers/finished_papers/IJAERDV03I0528370.Pdf.” International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development, vol. 3, no. 05, 2016, doi:10.21090/ijaerd.030517.
Maddie Pieper
Starbucks, an internationally and insanely popular coffee chain, announced to globally eliminate plastic straws from all of their locations by 2020. This announcement is in regards to the overwhelming amount of plastic in our ocean, and how it’s killing at least 100 million marine animals annually. So much plastic is dumped into our oceans, killing 700 species of animals. While Starbucks’ promise to ban plastic straws form their facilities won’t solely fix the problem, it will help decrease the amount of plastic in our oceans.
However, the cost of saving our ocean ecosystem is the price of the straw manufacturers. By converting to no straws, nearly 2,000 jobs would be lost in New York City, 8,000 in California, and 400 million dollars in economic activity. If no one is ordering plastic straws, the manufacturers will go out of business. Banning plastic straws sounds like a great plan when thinking short term, but long term, could it do more harm than good? The California State Water Resources Control Board released a study that said, “mere substitution would not result in reduced trash generation if such product substitution would be discarded in the same manner as the banned item” (The Daily Wire). Even though reusable straws are environmentally more friendly, if we continually dispose of them as we did prior to the ban, our oceans will still be affected by the waste. The table below shows the cost and effects of banning plastic straws in New York City alone. In total, it would cost approximately 91.3 million dollars to eliminate plastic straws from only one city.
See link here to table here for more information
The plastic straw ban has been controversial for years now, regaining popularity in the news due to Starbucks’ promise (Starbucks Newsroom). Plastic straws are something so ordinary and a part of our everyday culture, many wouldn’t think have how big of an impact they have on our earth and our economy. Are the jobs lost worth the reduction of the trash in the ocean, or will skipping the straw help us more in the long run?
Works Cited
Lockhart, Keely. “Plastic Straw Removed from Turtle's Nose by Marine Biologists in Heartbreaking Video .” The Telegraph, Telegraph Media Group, 22 Mar. 2016, www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2016/03/22/plastic-straw-removed-from-turtles-nose-by-marine-biologists-in/.
“Plastikmüll Im Meer.” Syrdallschoulen, portal.education.lu/syrdallschoulen/KIDS/News-fir-Kids/ArtMID/4828/ArticleID/560209/Plastikm252ll-im-Meer.
“Starbucks to Eliminate Plastic Straws Globally by 2020.” Starbucks Newsroom, 9 July 2018, news.starbucks.com/press-releases/starbucks-to-eliminate-plastic-straws-globally-by-2020.
“These 5 Marine Animals Are Dying Because of Our Plastic Trash ... Here's How We Can Help.” One Green Planet, 5 Feb. 2017, www.onegreenplanet.org/animalsandnature/marine-animals-are-dying-because-of-our-plastic-trash/.
“Http://Www.ijaerd.com/Papers/finished_papers/IJAERDV03I0528370.Pdf.” International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development, vol. 3, no. 05, 2016, doi:10.21090/ijaerd.030517.
Paid, Sick and Family Leave
Anika King
Economics B1
Paid Sick and Family Leave
Currently, there is an uprise of concerns over the ability to have paid sick/ family leave time. It’s increasing popularity has been a hot topic for debates since United States is one of the only countries that doesn’t provide this opportunity to it’s employers and employees. Therefore, some companies like Amazon have taken it into their own hands to provide for their employees. So far, it has shown many benefits for the company and may help support the economy.
First of all, we do have a small step in the right direction for paid leave provided by the FMLA which has shown to provide many benefits for people who use it. But, what are these benefits? “According to the Center for Economic and Policy Research, about 90% of employers reported that California’s paid family leave policies had either a positive effect or no effect on productivity and profit. Around 96% agreed that it decreased employee turnover and about 99% believed that it boosted employee morale (Penn Wharton University of Pennsylvania). Therefore, the benefits of paid sick/family leave would be tremendous. It would also benefit business instead of hurting them. In return, this helps grow the economy.
Some benefits companies have observed are fewer worker turnovers. This is beneficial because, the process of finding a new employee is very time consuming. You first need to recruit and/or have many applicants. Then, the additional time it takes for them to train in their field or get acclimated to the environment can take even more time. Therefore, by having a temporary substitution and paying someone on leave is much more beneficial. Paid leave would also help women stay in the workforce instead of leaving when wanting to pursue a family. Having a new born child and growing your family should be a moment of pure bliss not anxious nerves of how you will be able to support your family. Therefore, paid leave would be beneficial for many women in the workforce. Especially because many women don’t have a reliable male figure in the household anymore.

https://fairygodboss.com/maternity-leave-resource-center/international-perspective
As you can see America is falling behind for paid sick and family leave. Not very encouraging is it?
Now, imagine going to a restaurant and ordering your favorite mac and cheese...so creamy and delicious. Then later that night you figure out your chef who made the yummy dinner has the flu and was obviously touching your food. According to The New York Times, “Each week about 1.5 million Americans without paid sick leave go to work despite feeling ill.” Which if you think about it, that’s pretty gross. Even worse, the most common jobs where ill employees are likely to attend work because the opportunity cost of not going is too high are hospitals and restaurants. The two easiest places to spread germs and communicable diseases. By providing paid medical leave for employees it is much safer especially for customers and patients in hospitals who are very vulnerable to sickness due to their weakened immune system. A few states that offer paid sick leave to their employees have dramatically reduced flu cases per year. “Flu rates would fall 5 percent if paid sick leave were universal,” (New York Times). Besides, these facts imagine the increased access employee’s would have to doctors with paid work leave. Being able to see a doctor around a work schedule can be extremely difficult. This would help reduce this problem greatly.

http://newsroom.ucla.edu/releases/paid-family-medical-leave-in-the-united-states:-good-for-families-good-for-the-economy
Here are the countries that support paid sick leave and those who do not offer it to employees and employers.
Therefore, with the extensive amount of benefits that paid sick/family leave can offer...why shouldn’t we put this law into action? The benefits benefit everyone too, not just the person who stays home because they don’t feel good. This helps the employees, employers, and the economy. The increased support will help reduce worker-turnover, help keep women in the work force, and slow the spread of communicable diseases. The safety and practicality of this law are without a question beneficial. So, c’mon United States make a move on paid sick and family leave.
Works Cited
Denly, Carla. “Paid Family Medical Leave in the United States: Good for Families, Good for the Economy.” UCLA Newsroom, 28 Feb. 2018, newsroom.ucla.edu/releases/paid-family-medical-leave-in-the-united-states:-good-for-families-good-for-the-economy.
“Economic Benefits of Paid Sick and Family Leave.” Penn Wharton Public Policy Initative, publicpolicy.wharton.upenn.edu/live/news/2054-economic-benefits-of-paid-sick-and-family-leave.
Frakt, Austin. “The High Costs of Not Offering Paid Sick Leave.” The New York Times, The New York Times, 31 Oct. 2016, www.nytimes.com/2016/11/01/upshot/the-high-costs-of-not-offering-paid-sick-leave.html.
Machicado, Claudia Calderon. “The Business Case for Paid Leave and Paid Sick Days.” Center for American Progress, 20 Aug. 2014, www.americanprogress.org/issues/economy/news/2014/04/17/88243/the-business-case-for-paid-leave-and-paid-sick-days/.
Economics B1
Paid Sick and Family Leave
Currently, there is an uprise of concerns over the ability to have paid sick/ family leave time. It’s increasing popularity has been a hot topic for debates since United States is one of the only countries that doesn’t provide this opportunity to it’s employers and employees. Therefore, some companies like Amazon have taken it into their own hands to provide for their employees. So far, it has shown many benefits for the company and may help support the economy.
First of all, we do have a small step in the right direction for paid leave provided by the FMLA which has shown to provide many benefits for people who use it. But, what are these benefits? “According to the Center for Economic and Policy Research, about 90% of employers reported that California’s paid family leave policies had either a positive effect or no effect on productivity and profit. Around 96% agreed that it decreased employee turnover and about 99% believed that it boosted employee morale (Penn Wharton University of Pennsylvania). Therefore, the benefits of paid sick/family leave would be tremendous. It would also benefit business instead of hurting them. In return, this helps grow the economy.
Some benefits companies have observed are fewer worker turnovers. This is beneficial because, the process of finding a new employee is very time consuming. You first need to recruit and/or have many applicants. Then, the additional time it takes for them to train in their field or get acclimated to the environment can take even more time. Therefore, by having a temporary substitution and paying someone on leave is much more beneficial. Paid leave would also help women stay in the workforce instead of leaving when wanting to pursue a family. Having a new born child and growing your family should be a moment of pure bliss not anxious nerves of how you will be able to support your family. Therefore, paid leave would be beneficial for many women in the workforce. Especially because many women don’t have a reliable male figure in the household anymore.
https://fairygodboss.com/maternity-leave-resource-center/international-perspective
As you can see America is falling behind for paid sick and family leave. Not very encouraging is it?
Now, imagine going to a restaurant and ordering your favorite mac and cheese...so creamy and delicious. Then later that night you figure out your chef who made the yummy dinner has the flu and was obviously touching your food. According to The New York Times, “Each week about 1.5 million Americans without paid sick leave go to work despite feeling ill.” Which if you think about it, that’s pretty gross. Even worse, the most common jobs where ill employees are likely to attend work because the opportunity cost of not going is too high are hospitals and restaurants. The two easiest places to spread germs and communicable diseases. By providing paid medical leave for employees it is much safer especially for customers and patients in hospitals who are very vulnerable to sickness due to their weakened immune system. A few states that offer paid sick leave to their employees have dramatically reduced flu cases per year. “Flu rates would fall 5 percent if paid sick leave were universal,” (New York Times). Besides, these facts imagine the increased access employee’s would have to doctors with paid work leave. Being able to see a doctor around a work schedule can be extremely difficult. This would help reduce this problem greatly.
http://newsroom.ucla.edu/releases/paid-family-medical-leave-in-the-united-states:-good-for-families-good-for-the-economy
Here are the countries that support paid sick leave and those who do not offer it to employees and employers.
Therefore, with the extensive amount of benefits that paid sick/family leave can offer...why shouldn’t we put this law into action? The benefits benefit everyone too, not just the person who stays home because they don’t feel good. This helps the employees, employers, and the economy. The increased support will help reduce worker-turnover, help keep women in the work force, and slow the spread of communicable diseases. The safety and practicality of this law are without a question beneficial. So, c’mon United States make a move on paid sick and family leave.
Works Cited
Denly, Carla. “Paid Family Medical Leave in the United States: Good for Families, Good for the Economy.” UCLA Newsroom, 28 Feb. 2018, newsroom.ucla.edu/releases/paid-family-medical-leave-in-the-united-states:-good-for-families-good-for-the-economy.
“Economic Benefits of Paid Sick and Family Leave.” Penn Wharton Public Policy Initative, publicpolicy.wharton.upenn.edu/live/news/2054-economic-benefits-of-paid-sick-and-family-leave.
Frakt, Austin. “The High Costs of Not Offering Paid Sick Leave.” The New York Times, The New York Times, 31 Oct. 2016, www.nytimes.com/2016/11/01/upshot/the-high-costs-of-not-offering-paid-sick-leave.html.
Machicado, Claudia Calderon. “The Business Case for Paid Leave and Paid Sick Days.” Center for American Progress, 20 Aug. 2014, www.americanprogress.org/issues/economy/news/2014/04/17/88243/the-business-case-for-paid-leave-and-paid-sick-days/.
How does Hunting affect the Economy
Tyler Hintz
Econ Blog Post
Reuter
How Does Hunting Affect the Economy?
For millions of people around America and all around the world, hunting has become an addiction that flows through hunters veins and keeps them coming back to do the same thing with the same intensity and eagerness as the year before. Hunting is a lifestyle for many, but even for those that choose not to let an arrow fly or pull the trigger in the fall, hunting many still benefit them without them even knowing it. Hunting has a profound effect on the economy as it provides jobs at different outfitter stores around the nation, as well as a bunch of revenue that goes towards different purposes.

Even though it may not seem like a big business, hunting supports more than sixty-eight thousand jobs and has annual impact of some thirty-eight billion dollars on the economy. Hunting revenue primarily comes from the sale of licenses but it also is made from all of the people that buy the gear they need. Because there are so many different seasons of hunting, the sales of products and licenses can create profit throughout the whole year. Not just during the fall when most of the hunting seasons take place. Hunting also supports motels and tent companies stay in business when they take trips to different states for bigger hunts. Hunting itself has created its own line of outdoor stores like Cabelas and Gander Outdoors which is a big money maker.
No matter what the age, one thing is for sure. Hunting is hot and getting hotter. Did you know that some sixteen million Americans will hunt this year? The combined revenue alone from this will be a giant spike in the government's revenue over the next few months once hunting starts to heat up. Hunters spend an average of twenty-two billion dollars each season. All of this money spent on all of the gear means that hunting is good for all of those companies.
Below is a chart showing all of the sales in 1996 done by hunters as well as jobs that were created. Imagine the growth of the amount of hunters over the last twenty years and the amount this number has grown by.
As you can see hunting truly creates jobs and alot of revenue. As people around the world continue to find hunting as an interest, these numbers will simply continue to climb and big outfitters like Cabelas will continue to grow in sales, as well as the companies they endorse. So as we hunters continue to gear up and purchase annual licenses, the government will continue to receive revenue. And that is good for our economy.
“The Economic Importance of Hunting.” The Economic Importance of Hunting - California Department of Fish and Wildlife, www.dfg.ca.gov/wildlife/hunting/econ-hunting.html.
“Hunting in America - The Economy.” Protect The Harvest, 19 Nov. 2015, protecttheharvest.com/2014/11/14/hunting-america-economy/.
Econ Blog Post
Reuter
How Does Hunting Affect the Economy?
For millions of people around America and all around the world, hunting has become an addiction that flows through hunters veins and keeps them coming back to do the same thing with the same intensity and eagerness as the year before. Hunting is a lifestyle for many, but even for those that choose not to let an arrow fly or pull the trigger in the fall, hunting many still benefit them without them even knowing it. Hunting has a profound effect on the economy as it provides jobs at different outfitter stores around the nation, as well as a bunch of revenue that goes towards different purposes.
Even though it may not seem like a big business, hunting supports more than sixty-eight thousand jobs and has annual impact of some thirty-eight billion dollars on the economy. Hunting revenue primarily comes from the sale of licenses but it also is made from all of the people that buy the gear they need. Because there are so many different seasons of hunting, the sales of products and licenses can create profit throughout the whole year. Not just during the fall when most of the hunting seasons take place. Hunting also supports motels and tent companies stay in business when they take trips to different states for bigger hunts. Hunting itself has created its own line of outdoor stores like Cabelas and Gander Outdoors which is a big money maker.
No matter what the age, one thing is for sure. Hunting is hot and getting hotter. Did you know that some sixteen million Americans will hunt this year? The combined revenue alone from this will be a giant spike in the government's revenue over the next few months once hunting starts to heat up. Hunters spend an average of twenty-two billion dollars each season. All of this money spent on all of the gear means that hunting is good for all of those companies.
Below is a chart showing all of the sales in 1996 done by hunters as well as jobs that were created. Imagine the growth of the amount of hunters over the last twenty years and the amount this number has grown by.
US 1996 Hunting Economic Impacts
Deer
|
Migratory Birds
|
Upland Game Bird (Quail,
Pheasant, Grouse only) |
All Hunting
| |
Retail Sales
|
$10,324,904,373
|
$2,996,257,139
|
$1,895,704,348
|
$22,104,313,660
|
Multiplier Effect
|
$27,858,958,706
|
$8,154,525,482
|
$4,903,780,081
|
$60,998,344,806
|
Salaries and Wages
|
$7,200,082,463
|
$2,116,177,982
|
$1,201,073,493
|
$16,120,559,638
|
Jobs
|
331,904
|
95,748
|
55,546
|
704,601
|
State Sales Tax Revenues
|
$581,054,859
|
$178,480,197
|
$128,803,838
|
$1,068,110,791
|
State Income Tax Revenues
|
$148,594,333
|
$37,995,873
|
$22,524,049
|
$322,236,505
|
Fed. Income Tax Revenues
|
$763,392,226
|
$216,155,138
|
$125,587,037
|
$1,725,812,994
|
Retail Sales
|
Multiplier Effect
|
Earnings
|
Jobs
|
Sales Tax
|
State Income Tax
|
Fed. Income Tax
|
$982,097,906
|
$2,100,374,184
|
$618,208,449
|
26,802
|
$59,844,553
|
$6,688,258
|
$66,398,026
|
Source: “The Economic Importance of Hunting.” The Economic Importance of Hunting - California Department of Fish and Wildlife,
www.dfg.ca.gov/wildlife/hunting/econ-hunting.html.
www.dfg.ca.gov/wildlife/hunting/econ-hunting.html.
As you can see hunting truly creates jobs and alot of revenue. As people around the world continue to find hunting as an interest, these numbers will simply continue to climb and big outfitters like Cabelas will continue to grow in sales, as well as the companies they endorse. So as we hunters continue to gear up and purchase annual licenses, the government will continue to receive revenue. And that is good for our economy.
“The Economic Importance of Hunting.” The Economic Importance of Hunting - California Department of Fish and Wildlife, www.dfg.ca.gov/wildlife/hunting/econ-hunting.html.
“Hunting in America - The Economy.” Protect The Harvest, 19 Nov. 2015, protecttheharvest.com/2014/11/14/hunting-america-economy/.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)